5 Ways Calculate Profit
Introduction to Calculating Profit

Calculating profit is a crucial aspect of any business, as it helps entrepreneurs and managers understand the financial health of their organization. Profit is the amount of money left over after deducting the costs of producing and selling a product or service from the revenue generated. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate profit, highlighting the importance of each method and providing examples to illustrate their application.
Method 1: Gross Profit Calculation
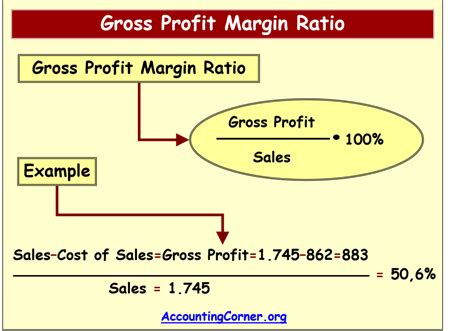
The gross profit calculation is the most basic method of determining profit. It involves subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the revenue generated by a business. The COGS includes the direct costs associated with producing a product or service, such as materials, labor, and overheads. The formula for calculating gross profit is: Gross Profit = Revenue - COGS For example, if a company generates 100,000 in revenue and has a COGS of 60,000, the gross profit would be $40,000.
Method 2: Operating Profit Calculation
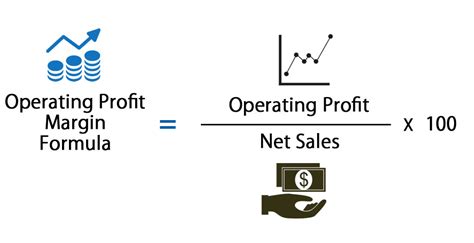
The operating profit calculation takes into account the operating expenses incurred by a business, in addition to the COGS. Operating expenses include salaries, rent, marketing, and other indirect costs. The formula for calculating operating profit is: Operating Profit = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses Using the same example as above, if the company has operating expenses of 15,000, the operating profit would be 25,000 (40,000 - 15,000).
Method 3: Net Profit Calculation

The net profit calculation is the most comprehensive method of determining profit, as it takes into account all the expenses incurred by a business, including taxes and interest. The formula for calculating net profit is: Net Profit = Operating Profit - Taxes - Interest For example, if the company has a tax expense of 5,000 and an interest expense of 2,000, the net profit would be 18,000 (25,000 - 5,000 - 2,000).
Method 4: Profit Margin Calculation

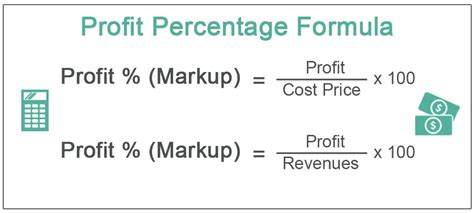
The profit margin calculation is used to express profit as a percentage of revenue. It helps businesses understand the profitability of their products or services. The formula for calculating profit margin is: Profit Margin = (Profit / Revenue) x 100 Using the same example as above, if the company has a net profit of 18,000 and revenue of 100,000, the profit margin would be 18% (18,000 / 100,000 x 100).
Method 5: Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation
The ROI calculation is used to evaluate the profitability of an investment or a business. It helps entrepreneurs and managers understand the return generated by their investments. The formula for calculating ROI is: ROI = (Gain from Investment - Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment For example, if an investor invests 10,000 in a business and generates a return of 15,000, the ROI would be 50% ((15,000 - 10,000) / $10,000).
📝 Note: These calculations are essential for businesses to understand their financial performance and make informed decisions about investments, pricing, and resource allocation.
In summary, calculating profit is a critical aspect of business management, and there are various methods to determine profit, including gross profit, operating profit, net profit, profit margin, and ROI. Each method provides valuable insights into the financial health of a business, and entrepreneurs and managers should use these calculations to inform their decision-making and drive business growth.
What is the difference between gross profit and operating profit?
+
Gross profit is the profit generated by a business after deducting the cost of goods sold, while operating profit is the profit generated after deducting operating expenses, in addition to the cost of goods sold.
How do I calculate net profit?

+
Net profit is calculated by subtracting taxes and interest from operating profit. The formula is: Net Profit = Operating Profit - Taxes - Interest.
What is the purpose of calculating profit margin?

+
The purpose of calculating profit margin is to express profit as a percentage of revenue, which helps businesses understand the profitability of their products or services.