5 Ways To Create Box Plot
Introduction to Box Plots
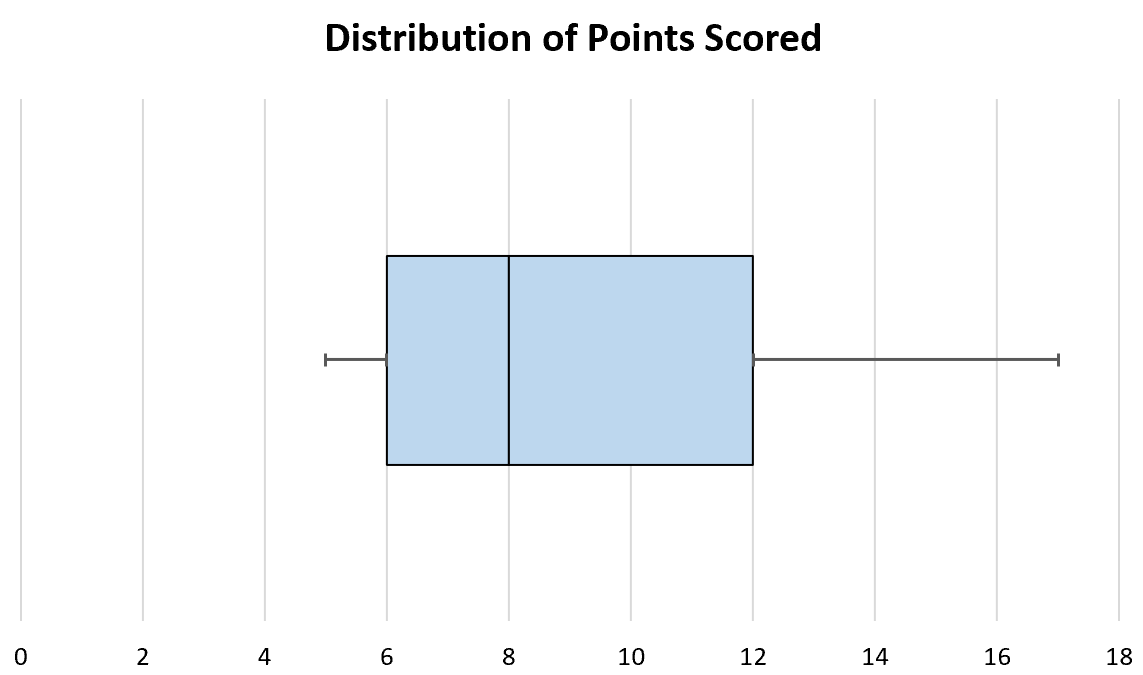
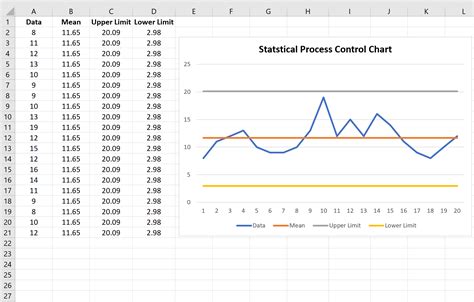
Box plots, also known as box-and-whisker plots, are a type of graphical representation used to display the distribution of a set of data. They are particularly useful for comparing the distribution of data across different groups or categories. A box plot typically consists of a box that represents the interquartile range (IQR), which is the difference between the 75th percentile (Q3) and the 25th percentile (Q1). The line inside the box represents the median, and the lines extending from the box are known as whiskers, which represent the range of the data.
Understanding the Components of a Box Plot
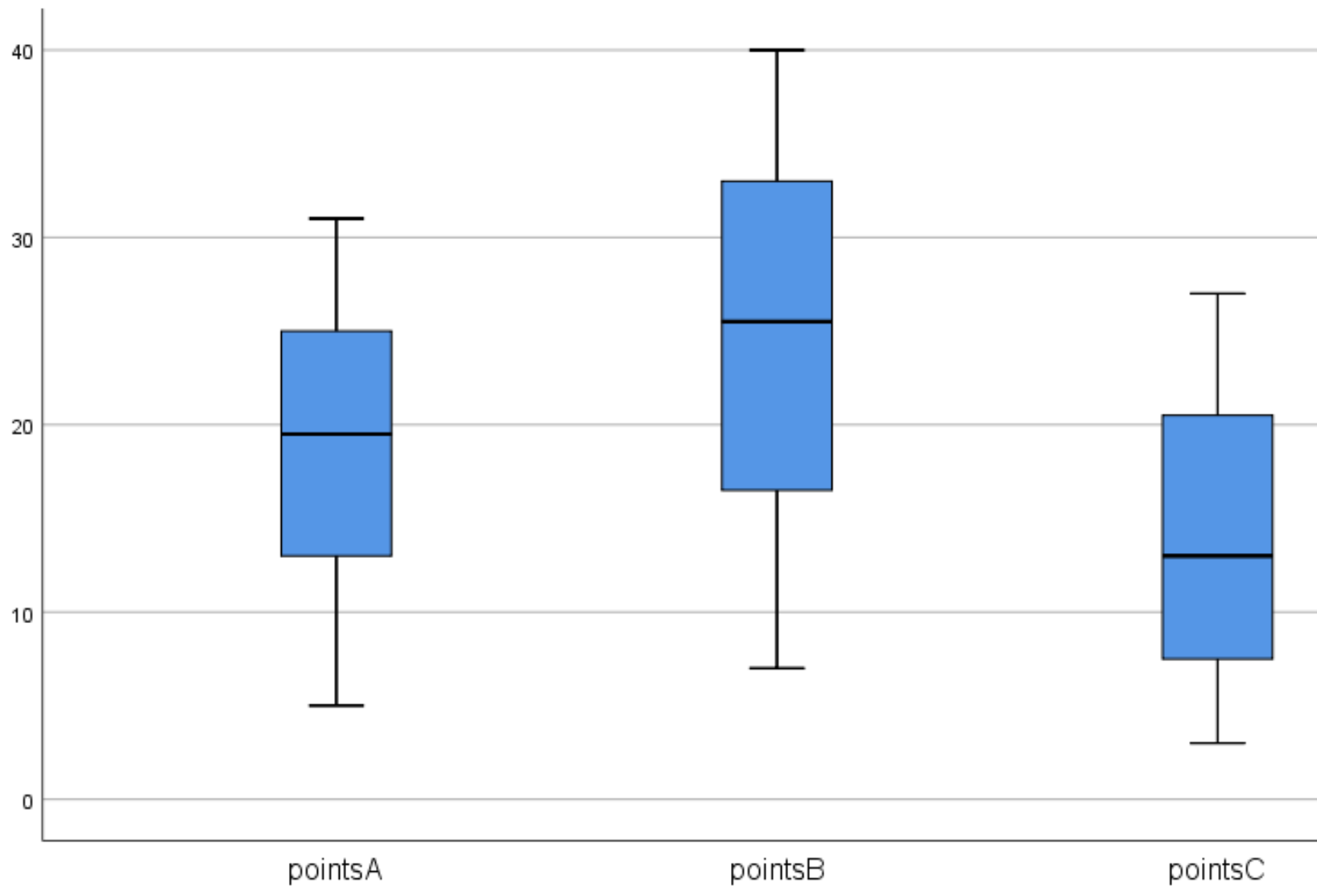
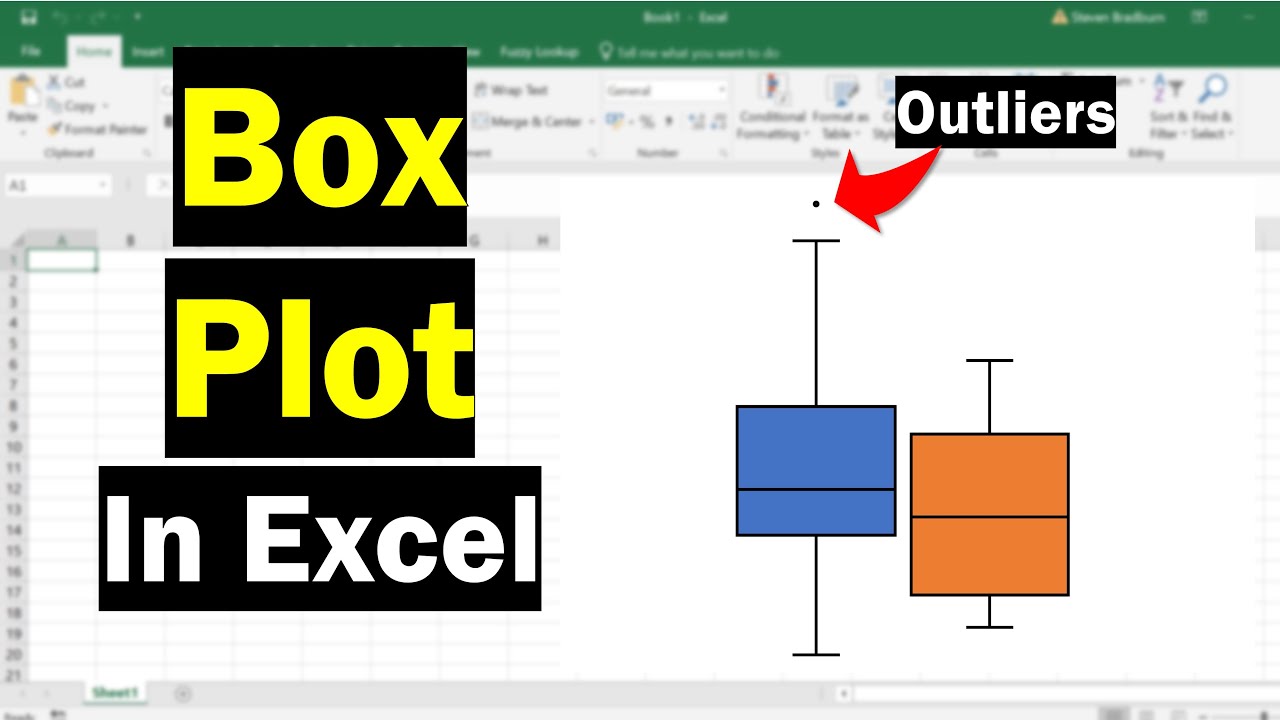
Before diving into the ways to create a box plot, it’s essential to understand the components of a box plot. The key components include: * Median: The line inside the box that represents the middle value of the data. * Quartiles: The 25th percentile (Q1) and the 75th percentile (Q3) that represent the lower and upper bounds of the box. * Interquartile Range (IQR): The difference between Q3 and Q1, which represents the spread of the middle 50% of the data. * Whiskers: The lines extending from the box that represent the range of the data. * Outliers: Data points that fall outside the whiskers, which can represent unusual or extreme values.
5 Ways to Create a Box Plot
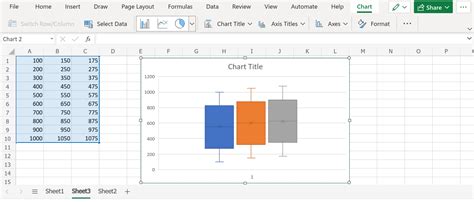
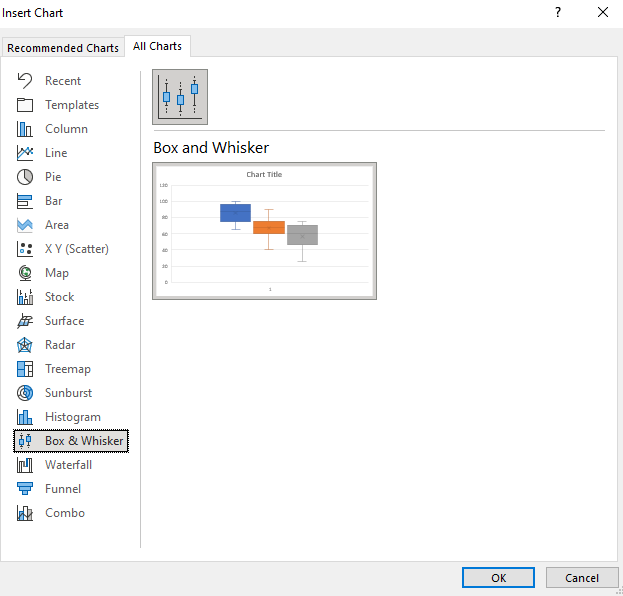
There are several ways to create a box plot, depending on the software or tool you are using. Here are five common methods: * Method 1: Using Excel + Enter your data into a column in Excel. + Go to the “Insert” tab and select “Chart.” + Choose the “Box and Whisker” chart type. + Customize the chart as needed. * Method 2: Using Python + Import the necessary libraries, such as matplotlib or seaborn. + Create a dataset or load your data into a pandas dataframe. + Use the boxplot function to create the plot. + Customize the plot as needed. * Method 3: Using R + Load your data into a dataframe. + Use the boxplot function to create the plot. + Customize the plot as needed. * Method 4: Using MATLAB + Load your data into a matrix or vector. + Use the boxplot function to create the plot. + Customize the plot as needed. * Method 5: Using Google Sheets + Enter your data into a column in Google Sheets. + Go to the “Insert” menu and select “Chart.” + Choose the “Box and Whisker” chart type. + Customize the chart as needed.
Example Use Cases
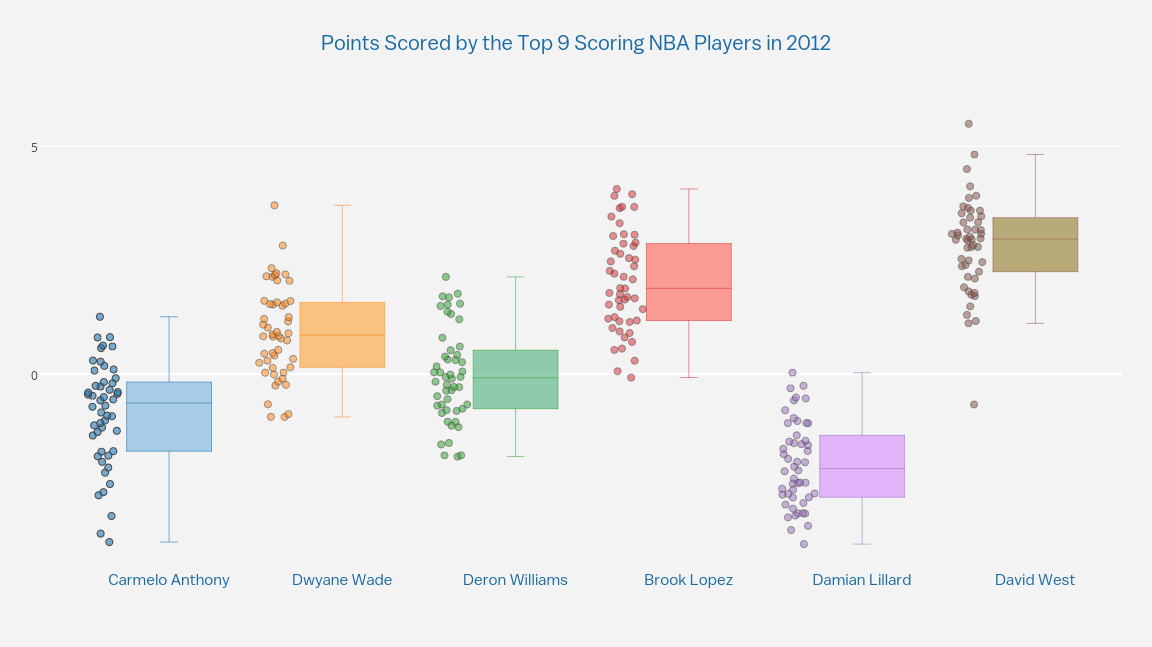
Box plots are useful in a variety of situations, such as: * Comparing the distribution of exam scores across different classes. * Analyzing the range of temperatures in different cities. * Visualizing the distribution of stock prices over time. * Identifying outliers in a dataset.
Best Practices for Creating Box Plots
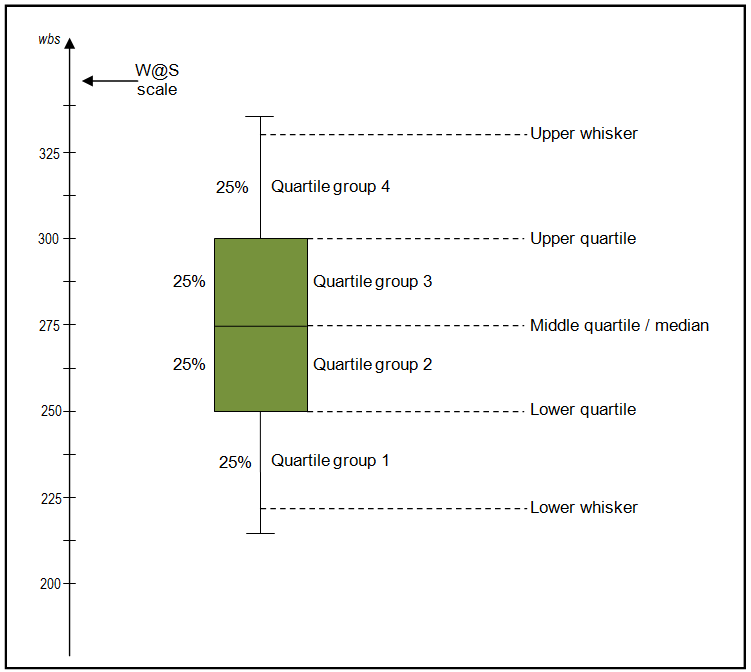
When creating box plots, keep the following best practices in mind: * Use a clear and concise title: Make sure the title accurately reflects the data being displayed. * Label the axes: Clearly label the x and y axes to avoid confusion. * Customize the plot: Adjust the plot as needed to make it easy to read and understand. * Avoid clutter: Keep the plot simple and uncluttered to avoid distracting from the data.
📊 Note: Box plots are most effective when used to compare the distribution of data across different groups or categories.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When creating box plots, there are several common mistakes to avoid, including: * Not labeling the axes: Failing to label the x and y axes can lead to confusion. * Not customizing the plot: Failing to adjust the plot as needed can make it difficult to read and understand. * Including too much data: Including too much data can make the plot cluttered and difficult to interpret. * Not checking for outliers: Failing to check for outliers can lead to incorrect conclusions.
| Method | Software/Tool | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Method 1 | Excel | Using the built-in box and whisker chart type |
| Method 2 | Python | Using the matplotlib or seaborn libraries |
| Method 3 | R | Using the boxplot function |
| Method 4 | MATLAB | Using the boxplot function |
| Method 5 | Google Sheets | Using the built-in box and whisker chart type |
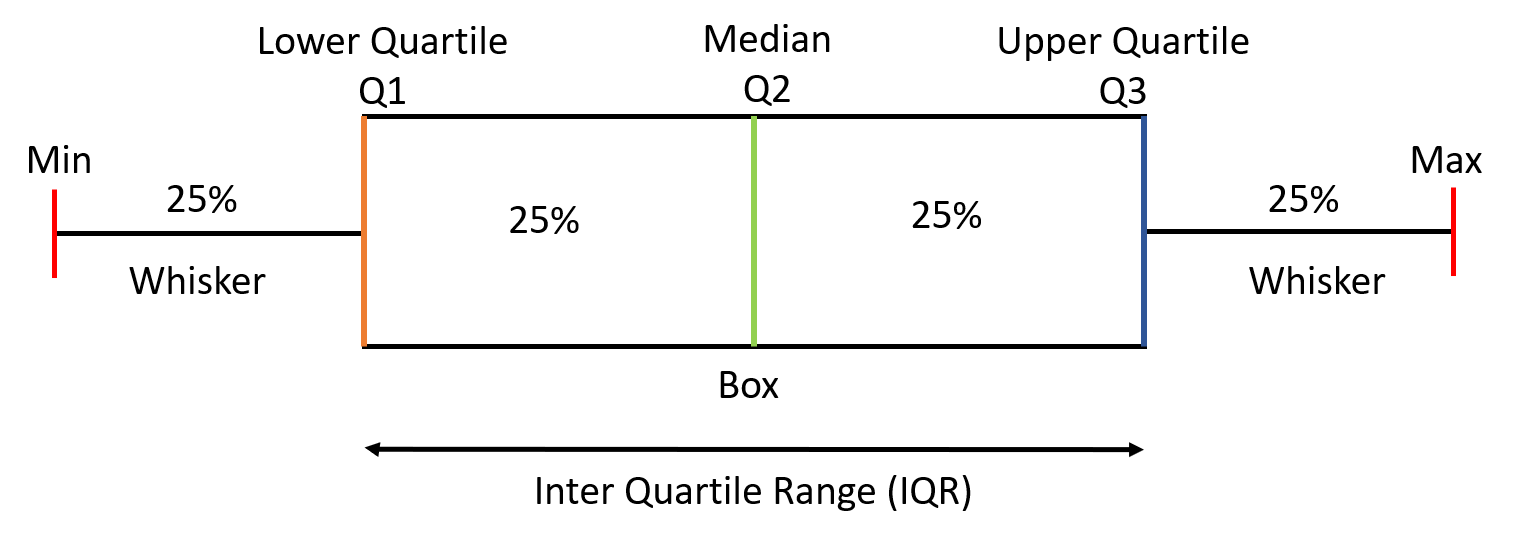
In summary, box plots are a powerful tool for visualizing and comparing the distribution of data. By following the best practices and avoiding common mistakes, you can create effective box plots that help you understand and communicate your data. Whether you’re using Excel, Python, R, MATLAB, or Google Sheets, there are several ways to create a box plot that meets your needs.
In the end, the key to creating effective box plots is to understand the components of the plot, choose the right software or tool, and customize the plot as needed. With practice and experience, you’ll become proficient in creating box plots that help you extract insights and meaning from your data.
What is a box plot?
+
A box plot is a graphical representation used to display the distribution of a set of data. It consists of a box that represents the interquartile range (IQR), a line inside the box that represents the median, and lines extending from the box that represent the range of the data.
What are the components of a box plot?
+
The key components of a box plot include the median, quartiles, interquartile range (IQR), whiskers, and outliers.
How do I create a box plot in Excel?

+
To create a box plot in Excel, enter your data into a column, go to the “Insert” tab, select “Chart,” and choose the “Box and Whisker” chart type. Customize the chart as needed.