5 Ways Measure Correlation
Introduction to Correlation Measurement
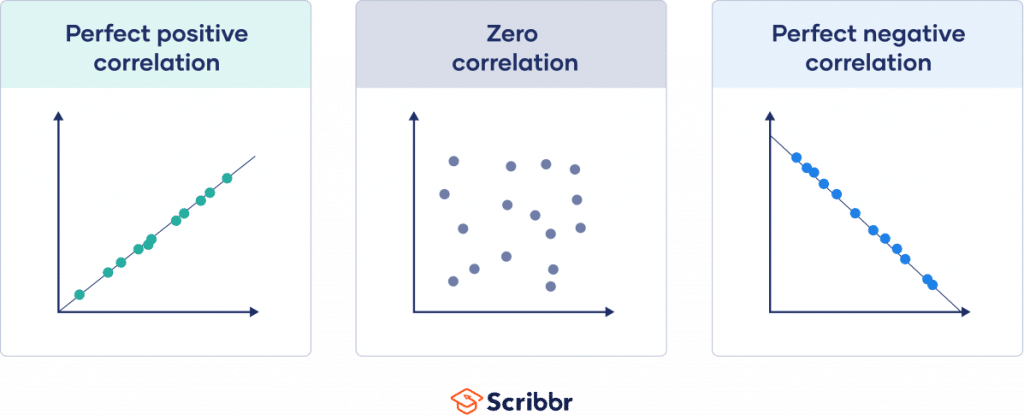
Correlation is a statistical measure that expresses the extent to which two variables change together. If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then the correlation between the variables is positive. On the other hand, if an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then the correlation between the variables is negative. Measuring correlation is crucial in various fields such as finance, medicine, and social sciences to understand the relationships between different variables. In this article, we will discuss 5 ways to measure correlation and their applications.
1. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
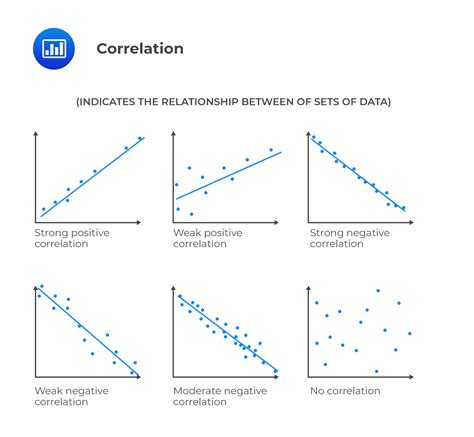
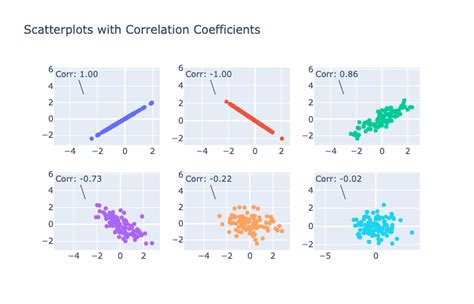
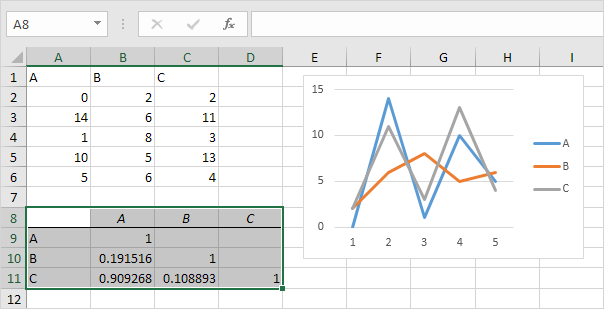
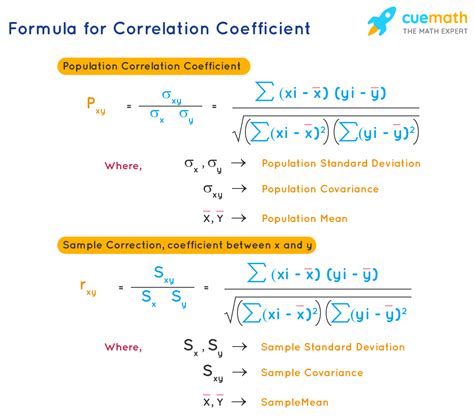
The Pearson correlation coefficient, often denoted as r, is a widely used measure of correlation. It measures the linear relationship between two continuous variables. The value of r ranges from -1 to 1, where 1 indicates a perfect positive linear relationship, -1 indicates a perfect negative linear relationship, and 0 indicates no linear relationship. The Pearson correlation coefficient is calculated using the following formula: [ r = \frac{\sum{(x_i - \bar{x})(y_i - \bar{y})}}{\sqrt{\sum{(x_i - \bar{x})^2}} \sqrt{\sum{(y_i - \bar{y})^2}}} ] where (x_i) and (y_i) are individual data points, (\bar{x}) and (\bar{y}) are the means of the two variables.
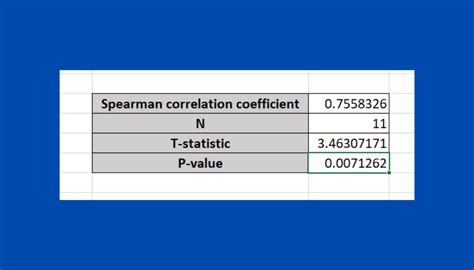
2. Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient
The Spearman rank correlation coefficient is a non-parametric measure of correlation that assesses the relationship between two variables by ranking the data. It is used when the data is not normally distributed or when the relationship between the variables is not linear. The Spearman correlation coefficient is calculated using the following formula: [ \rho = 1 - \frac{6 \sum{d_i^2}}{n(n^2 - 1)} ] where (d_i) is the difference between the ranks of the two variables for each data point, and n is the number of data points.
3. Kendall Tau Correlation Coefficient
The Kendall tau correlation coefficient is another non-parametric measure of correlation that assesses the relationship between two variables by counting the number of concordant and discordant pairs. It is used when the data is not normally distributed or when the relationship between the variables is not linear. The Kendall tau correlation coefficient is calculated using the following formula: [ \tau = \frac{N_c - N_d}{\sqrt{(N_c + N_d + T_x)(N_c + N_d + T_y)}} ] where (N_c) is the number of concordant pairs, (N_d) is the number of discordant pairs, (T_x) is the number of ties in the x-variable, and (T_y) is the number of ties in the y-variable.
4. Point-Biserial Correlation Coefficient
The point-biserial correlation coefficient is used to measure the correlation between a continuous variable and a binary variable. It is calculated using the following formula: [ r_{pb} = \frac{M_1 - M_0}{s} \sqrt{\frac{n_1 n_0}{n^2}} ] where (M_1) and (M_0) are the means of the continuous variable for the two groups, (s) is the standard deviation of the continuous variable, (n_1) and (n_0) are the sample sizes of the two groups, and n is the total sample size.
5. Phi Correlation Coefficient

The phi correlation coefficient is used to measure the correlation between two binary variables. It is calculated using the following formula: [ \phi = \frac{ad - bc}{\sqrt{(a + b)(a + c)(b + d)(c + d)}} ] where a, b, c, and d are the frequencies of the four possible combinations of the two binary variables.
📝 Note: The choice of correlation coefficient depends on the level of measurement of the variables and the nature of the relationship between them.
In conclusion, measuring correlation is essential in understanding the relationships between different variables. The 5 ways to measure correlation discussed in this article, namely the Pearson correlation coefficient, Spearman rank correlation coefficient, Kendall tau correlation coefficient, point-biserial correlation coefficient, and phi correlation coefficient, each have their own applications and are used in various fields to analyze the relationships between variables. By choosing the right correlation coefficient, researchers and analysts can gain valuable insights into the relationships between variables and make informed decisions.
What is the difference between Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients?
+
The Pearson correlation coefficient measures the linear relationship between two continuous variables, while the Spearman rank correlation coefficient measures the relationship between two variables by ranking the data.
When to use the Kendall tau correlation coefficient?
+
The Kendall tau correlation coefficient is used when the data is not normally distributed or when the relationship between the variables is not linear.
What is the point-biserial correlation coefficient used for?
+
The point-biserial correlation coefficient is used to measure the correlation between a continuous variable and a binary variable.