5 Ways Compute Years
Introduction to Calculating Compute Years
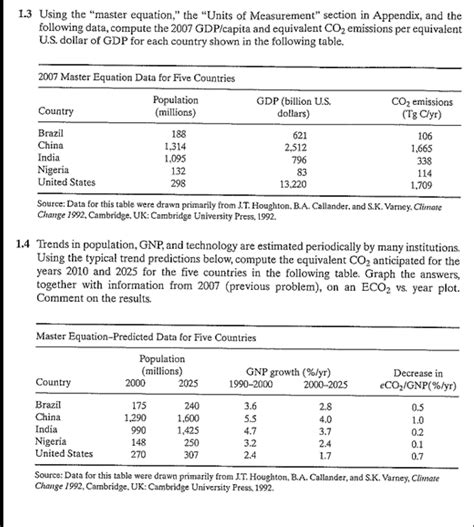
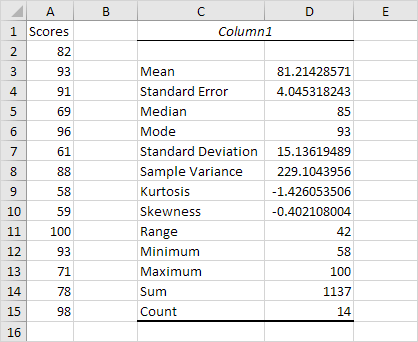
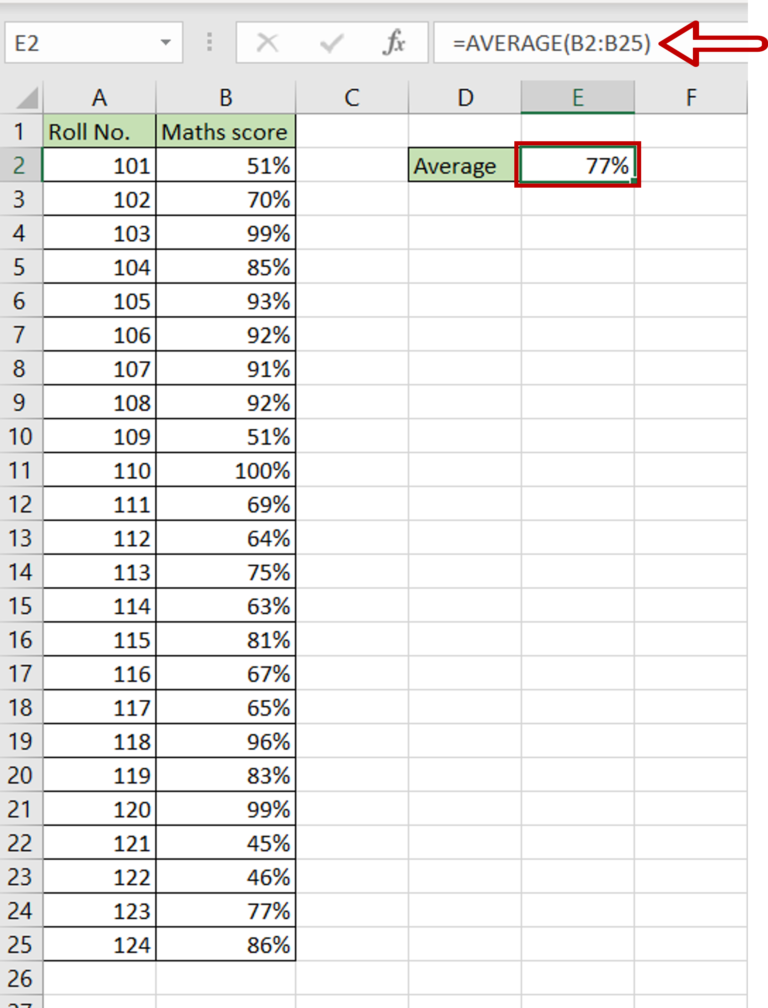
Calculating compute years is a complex process that involves understanding various factors such as processing power, memory, and storage. Compute years are a measure of the amount of computational work that can be performed by a machine or a system over a certain period. In this article, we will explore 5 ways to calculate compute years, highlighting the importance of each method and providing examples to illustrate their application.
Method 1: Using FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second)
One way to calculate compute years is by using the FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second) method. This method involves measuring the number of floating-point operations that a machine can perform per second. FLOPS is a common metric used to evaluate the performance of supercomputers and other high-performance computing systems. To calculate compute years using FLOPS, you need to know the total number of FLOPS performed by the machine over a certain period, usually a year.
Method 2: Using MIPS (Millions of Instructions Per Second)

Another method for calculating compute years is by using MIPS (Millions of Instructions Per Second). This method involves measuring the number of instructions that a machine can execute per second. MIPS is a common metric used to evaluate the performance of CPUs and other computing systems. To calculate compute years using MIPS, you need to know the total number of MIPS performed by the machine over a certain period, usually a year.
Method 3: Using Compute Cycles
Compute cycles refer to the number of times a machine can perform a specific task or operation over a certain period. This method involves measuring the number of compute cycles performed by a machine over a certain period, usually a year. To calculate compute years using compute cycles, you need to know the total number of compute cycles performed by the machine over a certain period.
Method 4: Using Clock Speed

Clock speed refers to the rate at which a machine’s clock ticks, usually measured in Hz (hertz). This method involves measuring the clock speed of a machine and using it to calculate the number of compute years. To calculate compute years using clock speed, you need to know the clock speed of the machine and the total number of seconds in a year.
Method 5: Using Benchmarking Tests

Benchmarking tests involve running a series of standardized tests on a machine to evaluate its performance. This method involves running benchmarking tests on a machine and using the results to calculate the number of compute years. To calculate compute years using benchmarking tests, you need to know the results of the benchmarking tests and the total number of seconds in a year.
💡 Note: When calculating compute years, it's essential to consider factors such as processing power, memory, and storage to ensure accurate results.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| FLOPS | Measures the number of floating-point operations per second |
| MIPS | Measures the number of instructions per second |
| Compute Cycles | Measures the number of times a machine can perform a specific task or operation |
| Clock Speed | Measures the rate at which a machine's clock ticks |
| Benchmarking Tests | Measures the performance of a machine using standardized tests |

In summary, calculating compute years involves using various methods such as FLOPS, MIPS, compute cycles, clock speed, and benchmarking tests. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific use case and requirements. By understanding these methods and their applications, you can accurately calculate compute years and make informed decisions about your computing needs.
What is the most common method for calculating compute years?

+
The most common method for calculating compute years is using FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second).
What is the difference between FLOPS and MIPS?
+
FLOPS measures the number of floating-point operations per second, while MIPS measures the number of instructions per second.
Can I use benchmarking tests to calculate compute years?
+
Yes, you can use benchmarking tests to calculate compute years by running standardized tests on a machine and using the results to estimate the number of compute years.