5 Ways To Separate
Introduction to Separation Techniques

Separation techniques are essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and engineering. These techniques enable us to isolate specific components from a mixture, which is crucial for further analysis, processing, or utilization. In this blog post, we will discuss five key methods used for separation, highlighting their principles, applications, and importance.
1. Distillation

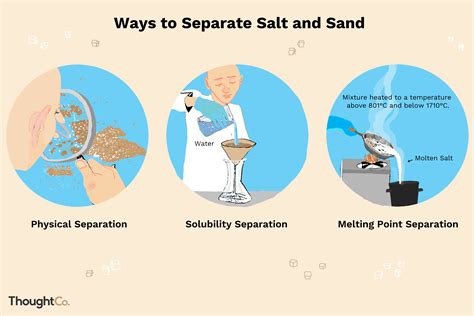
Distillation is a widely used separation technique that relies on the differences in boiling points of the components in a mixture. This method involves heating the mixture to produce vapor, which is then condensed and collected as a separate component. Distillation is commonly applied in the production of alcoholic beverages, petroleum refining, and water purification. There are several types of distillation, including simple distillation, fractional distillation, and vacuum distillation, each with its specific applications and advantages.
2. Chromatography
Chromatography is a powerful analytical technique used to separate, identify, and quantify the components in a mixture. It works on the principle of differential distribution of the components between two phases: a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Chromatography has various applications in biomedical research, food analysis, and environmental monitoring. The different types of chromatography include gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, and paper chromatography, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
3. Filtration
Filtration is a simple yet effective separation technique used to remove particulate matter from a fluid (liquid or gas) by passing it through a porous material, known as a filter. The filter traps the particles, allowing the clean fluid to pass through. Filtration is widely used in water treatment, air purification, and industrial processes. There are different types of filters, including membrane filters, cartridge filters, and bag filters, each designed for specific applications and particle sizes.
4. Centrifugation

Centrifugation is a separation technique that uses centrifugal force to separate particles of different densities or sizes from a mixture. This method involves spinning the mixture at high speeds, causing the particles to settle at different rates. Centrifugation is commonly used in biological research, medical diagnostics, and industrial processes. There are various types of centrifuges, including laboratory centrifuges, industrial centrifuges, and ultracentrifuges, each with its specific applications and capabilities.
5. Crystallization

Crystallization is a separation technique used to obtain pure solids from a solution. This method involves cooling the solution slowly, allowing the solute to form crystals, which can then be separated from the mother liquor. Crystallization is widely used in the production of pharmaceuticals, foods, and chemicals. The different types of crystallization include solvent crystallization, melt crystallization, and freeze crystallization, each with its unique advantages and applications.
💡 Note: The choice of separation technique depends on the specific application, the properties of the components, and the desired level of purity.
In summary, separation techniques are crucial in various fields, enabling us to isolate specific components from mixtures. The five methods discussed in this blog post, including distillation, chromatography, filtration, centrifugation, and crystallization, are widely used and have significant applications in industry, research, and everyday life. Understanding these techniques is essential for advancing our knowledge and capabilities in various fields.
What is the main principle of distillation?
+
Distillation relies on the differences in boiling points of the components in a mixture.
What are the main applications of chromatography?

+
Chromatography has various applications in biomedical research, food analysis, and environmental monitoring.
What is the purpose of filtration in water treatment?

+
Filtration is used to remove particulate matter from water, making it safe for consumption.