5 Ways To Find Relative Frequency
Introduction to Relative Frequency
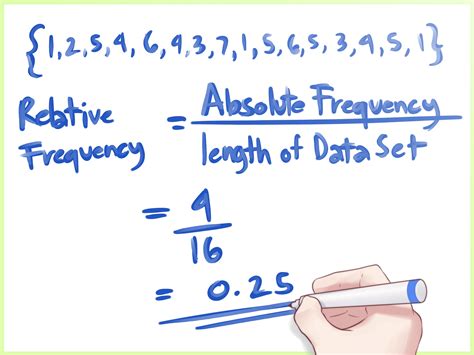
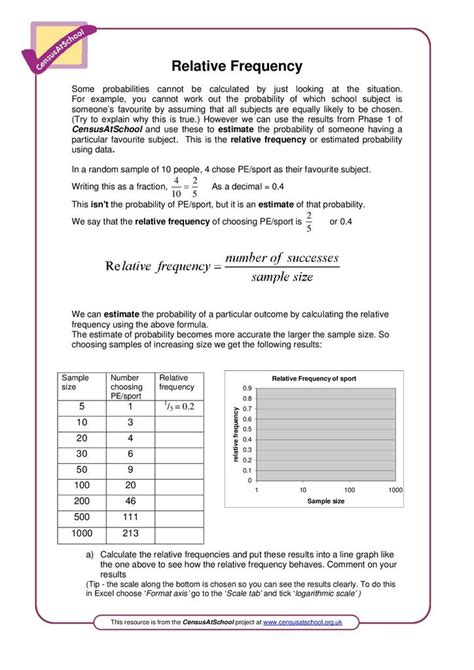
Relative frequency is a statistical concept that refers to the number of times an event occurs in a given sample or population, expressed as a proportion or percentage of the total number of events. It is an important concept in statistics and data analysis, as it helps to understand and describe the distribution of data. In this article, we will explore five ways to find relative frequency, along with examples and explanations to help you understand the concept better.
What is Relative Frequency?
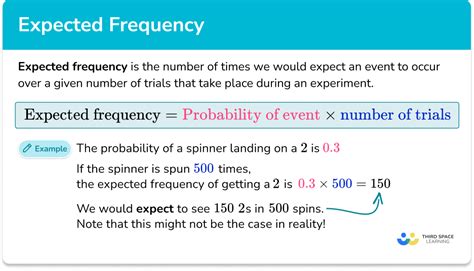
Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the frequency of an event by the total number of events in a sample or population. It can be expressed as a proportion (a value between 0 and 1) or as a percentage (a value between 0% and 100%). For example, if a survey of 100 people finds that 20 people prefer a certain brand of coffee, the relative frequency of people who prefer that brand is 20⁄100 = 0.2 or 20%.
5 Ways to Find Relative Frequency
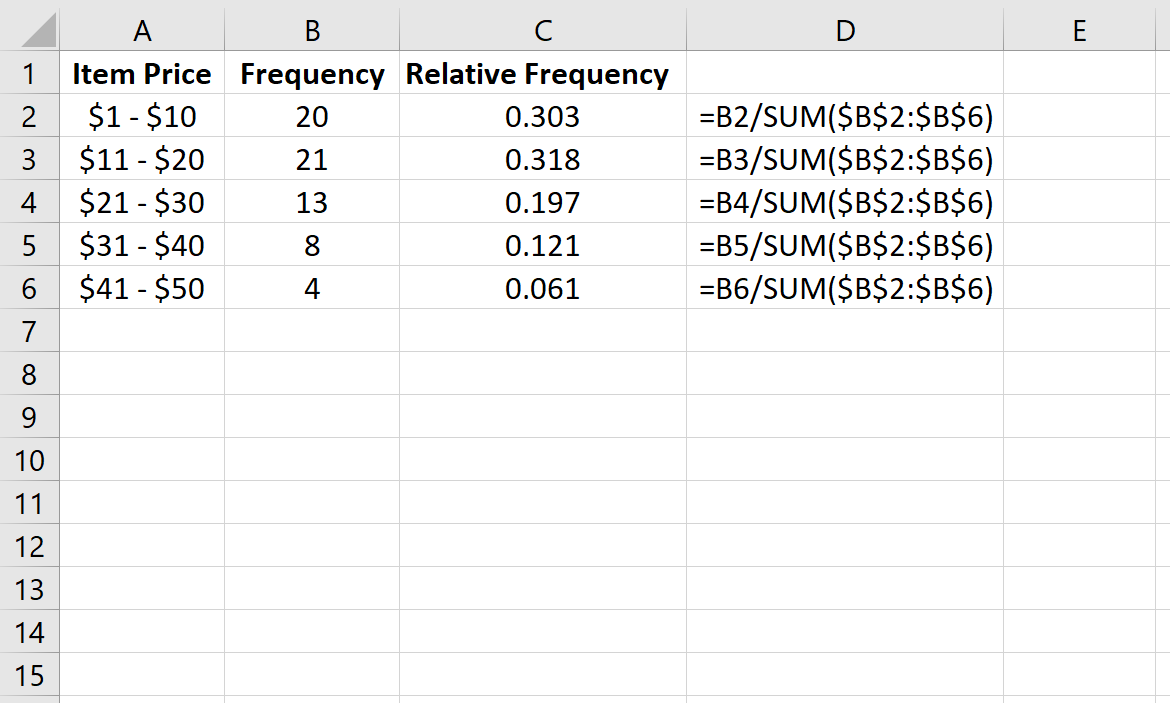
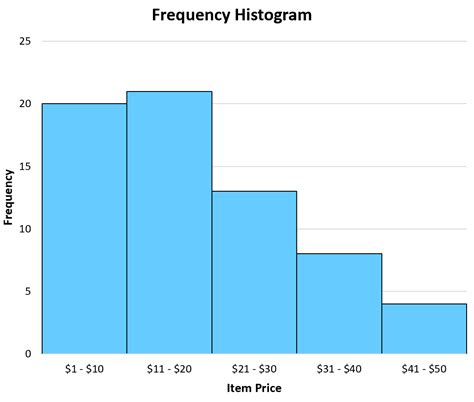
Here are five ways to find relative frequency: * Using a Frequency Table: A frequency table is a table that shows the frequency of each event or category in a sample or population. To find the relative frequency, divide the frequency of each event by the total number of events. * Using a Histogram: A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of data. To find the relative frequency, measure the area of each bar in the histogram and divide it by the total area of all the bars. * Using a Pie Chart: A pie chart is a circular graph that shows the proportion of each event or category in a sample or population. To find the relative frequency, measure the angle of each slice in the pie chart and divide it by 360 degrees (the total angle of the circle). * Using a Bar Chart: A bar chart is a graphical representation of the frequency of each event or category in a sample or population. To find the relative frequency, measure the height of each bar and divide it by the total height of all the bars. * Using a Formula: The relative frequency can be calculated using the formula: relative frequency = (frequency of an event) / (total number of events).
📝 Note: The relative frequency can be expressed as a proportion or a percentage, depending on the context and the purpose of the analysis.
Examples of Relative Frequency
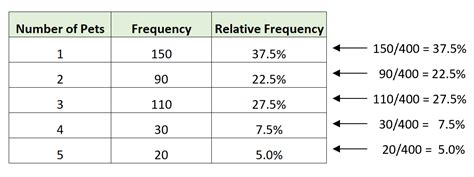
Here are some examples of relative frequency:
| Event | Frequency | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Favorite color: red | 20 | 0.2 or 20% |
| Favorite color: blue | 30 | 0.3 or 30% |
| Favorite color: green | 50 | 0.5 or 50% |
In this example, the relative frequency of people who prefer the color red is 20⁄100 = 0.2 or 20%, the relative frequency of people who prefer the color blue is 30⁄100 = 0.3 or 30%, and the relative frequency of people who prefer the color green is 50⁄100 = 0.5 or 50%.
Importance of Relative Frequency
Relative frequency is an important concept in statistics and data analysis, as it helps to understand and describe the distribution of data. It can be used to identify patterns and trends in the data, compare the frequency of different events, and make predictions about future events. Relative frequency can also be used to create graphical representations of the data, such as histograms, pie charts, and bar charts, which can help to visualize and communicate the results of the analysis.
In summary, relative frequency is a statistical concept that refers to the number of times an event occurs in a given sample or population, expressed as a proportion or percentage of the total number of events. There are five ways to find relative frequency: using a frequency table, using a histogram, using a pie chart, using a bar chart, and using a formula. Relative frequency is an important concept in statistics and data analysis, as it helps to understand and describe the distribution of data, identify patterns and trends, compare the frequency of different events, and make predictions about future events.
What is relative frequency?
+
Relative frequency is a statistical concept that refers to the number of times an event occurs in a given sample or population, expressed as a proportion or percentage of the total number of events.
How is relative frequency calculated?

+
Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the frequency of an event by the total number of events in a sample or population.
What are the five ways to find relative frequency?
+
The five ways to find relative frequency are: using a frequency table, using a histogram, using a pie chart, using a bar chart, and using a formula.



