5 Ways To Graph

Introduction to Graphing
Graphing is a fundamental concept in mathematics and data analysis, used to visualize and understand the relationships between different variables. There are various methods to graph data, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we will explore five ways to graph, including their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
1. Line Graphs
Line graphs are one of the most common types of graphs used to display data. They consist of a series of points connected by lines, showing the trend of the data over time or across different categories. Line graphs are useful for displaying continuous data, such as temperature, stock prices, or website traffic. The main advantage of line graphs is that they can show the direction and magnitude of changes in the data. However, they can be misleading if the data is not continuous or if there are large gaps between the data points.
2. Bar Graphs

Bar graphs are used to compare categorical data across different groups. They consist of bars of different lengths, each representing a category. Bar graphs are useful for displaying discrete data, such as the number of sales, website visitors, or customer satisfaction ratings. The main advantage of bar graphs is that they can be used to compare multiple categories side by side. However, they can be cluttered and difficult to read if there are too many categories.
3. Pie Charts
Pie charts are circular graphs used to show how different categories contribute to a whole. They consist of slices of a circle, each representing a category. Pie charts are useful for displaying proportional data, such as the market share of different companies or the percentage of website traffic from different sources. The main advantage of pie charts is that they can be used to show how different categories fit into a larger whole. However, they can be difficult to read and compare if there are too many categories.
4. Scatter Plots
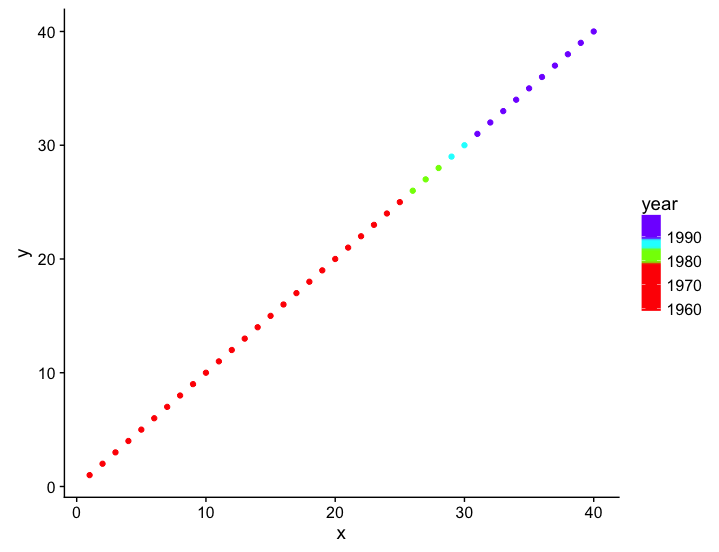
Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two continuous variables. They consist of points on a grid, each representing a data point. Scatter plots are useful for displaying the correlation between two variables, such as the relationship between temperature and humidity or the relationship between website traffic and engagement. The main advantage of scatter plots is that they can be used to identify patterns and relationships in the data. However, they can be cluttered and difficult to read if there are too many data points.
5. Histograms
Histograms are used to show the distribution of continuous data. They consist of bars of different lengths, each representing a range of values. Histograms are useful for displaying the frequency of different values in a dataset, such as the distribution of exam scores or the distribution of website traffic. The main advantage of histograms is that they can be used to identify patterns and trends in the data. However, they can be misleading if the bins are not chosen carefully.
📝 Note: When choosing a graph type, it's essential to consider the type of data, the purpose of the graph, and the audience. Different graph types are suited for different types of data and purposes, and choosing the wrong graph type can lead to misleading or confusing results.
In addition to these five graph types, there are many other types of graphs and visualization tools available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The key to effective graphing is to choose the right graph type for the data and purpose, and to use it in a way that is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
The following table summarizes the five graph types discussed in this article:
| Graph Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Graphs | Show trends over time or across categories | Show direction and magnitude of changes | Can be misleading if data is not continuous |
| Bar Graphs | Compare categorical data across groups | Can compare multiple categories side by side | Can be cluttered and difficult to read |
| Pie Charts | Show how categories contribute to a whole | Show how categories fit into a larger whole | Can be difficult to read and compare |
| Scatter Plots | Show relationship between two continuous variables | Can identify patterns and relationships | Can be cluttered and difficult to read |
| Histograms | Show distribution of continuous data | Can identify patterns and trends | Can be misleading if bins are not chosen carefully |

In summary, graphing is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding data. By choosing the right graph type and using it effectively, we can gain insights into the relationships and trends in the data, and make informed decisions based on that information.
What is the purpose of graphing in data analysis?
+
The purpose of graphing in data analysis is to visualize and understand the relationships and trends in the data, and to gain insights that can inform decision-making.
What are the different types of graphs used in data analysis?
+
There are several types of graphs used in data analysis, including line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
How do I choose the right graph type for my data?
+
To choose the right graph type, consider the type of data, the purpose of the graph, and the audience. Different graph types are suited for different types of data and purposes, and choosing the wrong graph type can lead to misleading or confusing results.