5 Ways To Add Footnotes

Introduction to Footnotes

When writing academic papers, articles, or even blog posts, it’s often necessary to include additional information that doesn’t fit neatly into the main body of the text. This is where footnotes come in – a way to provide further context, cite sources, or offer tangential information without disrupting the flow of the main content. In this article, we’ll explore five ways to add footnotes to your writing, ensuring that you can effectively communicate your ideas and provide readers with the additional information they might need.
Understanding the Purpose of Footnotes
Before diving into the methods of adding footnotes, it’s essential to understand their purpose. Footnotes serve several functions: - They provide a way to cite sources, giving credit to the original authors of ideas, data, or quotes. - They allow for the inclusion of additional information that might be interesting but isn’t crucial to understanding the main argument. - They can be used to define terms or explain concepts in more detail without cluttering the main text. - They offer a means to engage in a dialogue with other scholars or authors, responding to their ideas or critiques.
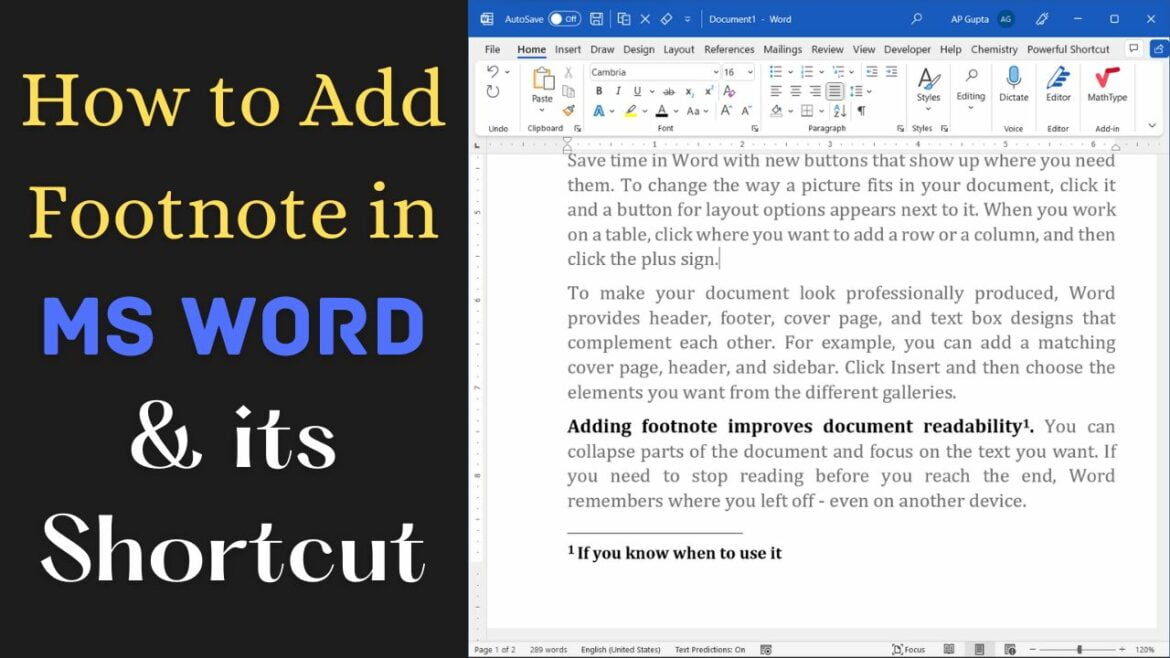
Method 1: Using Word Processing Software

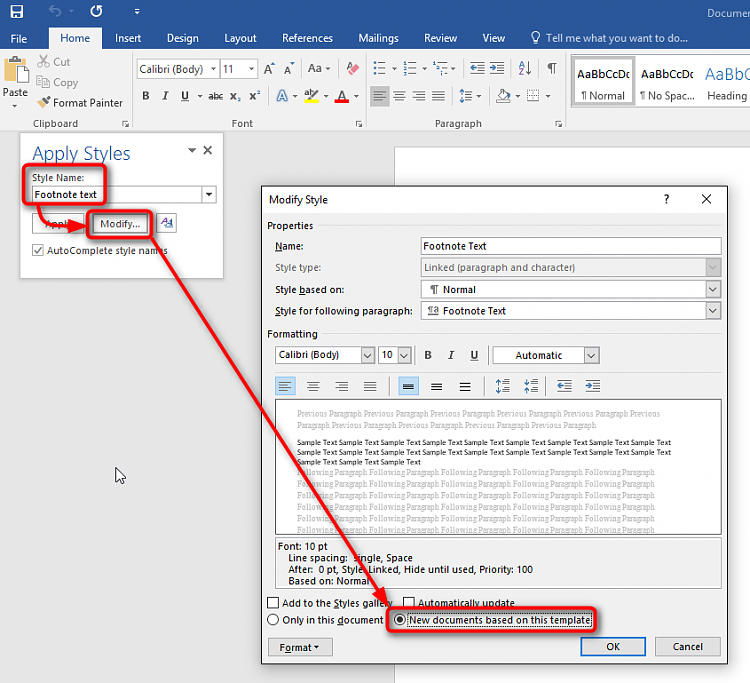
Most word processing software, such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs, includes a feature to insert footnotes directly into your document. Here’s how you can do it: - Place your cursor where you want to insert the footnote in the document. - Go to the “References” tab in Microsoft Word or the “Insert” menu in Google Docs. - Click on “Insert Footnote” in Word or “Footnote” in Google Docs. - A number will appear in the text, and you will be taken to the footnote area at the bottom of the page, where you can type your footnote.
📝 Note: When using word processing software, ensure that the footnote feature is set to automatically number and format your footnotes for consistency.
Method 2: Manual Insertion
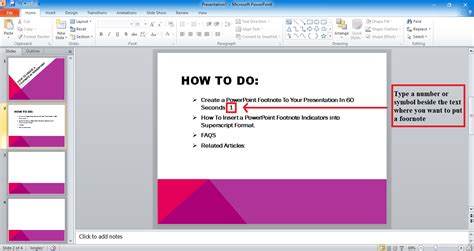
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach or are working in a plain text environment, footnotes can be manually inserted: - Decide on a numbering system (usually starting from 1) and place the corresponding number in superscript next to the relevant text. - At the bottom of the page (or the end of the document, depending on your citation style), insert a horizontal line to separate the footnotes from the main text. - Below this line, start your list of footnotes, with each footnote corresponding to the number in the text.
Method 3: Using LaTeX
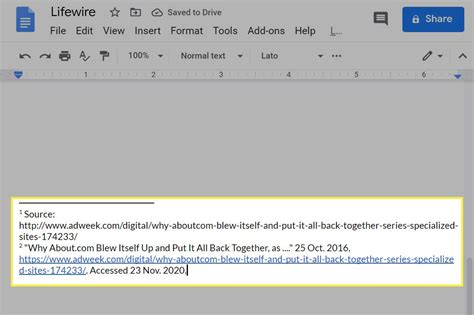
For academic and technical writing, especially in fields like mathematics, physics, and computer science, LaTeX is a popular document preparation system. Adding footnotes in LaTeX is straightforward: - Use the
\footnote command followed by the text of your footnote in curly brackets: \footnote{Your footnote text here}.
- LaTeX will automatically number and place the footnote at the bottom of the page.
Method 4: HTML Footnotes for Web Content

When creating content for the web, such as blog posts or articles, you can use HTML to add footnotes: - Use the
<sup> tag to superscript the footnote number in the text: <sup>1</sup>.
- Create a footnote section at the bottom of the page, using <p> or <li> tags to list each footnote, corresponding to the numbers in the text.
- You can also use CSS to style your footnotes, making them more visually appealing and easier to read.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Word Processing Software | Using built-in footnote features in programs like Microsoft Word or Google Docs. |
| Manual Insertion | Manually placing superscript numbers in the text and listing footnotes at the bottom of the page. |
| LaTeX | Utilizing the `\footnote` command in LaTeX documents. |
| HTML for Web Content | Using HTML tags like `` and CSS for styling footnotes on web pages. |
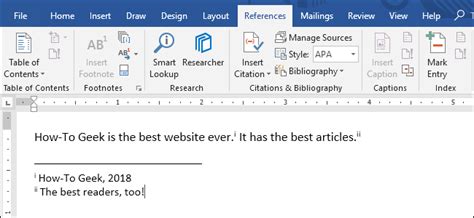
Method 5: Using Citation Management Tools
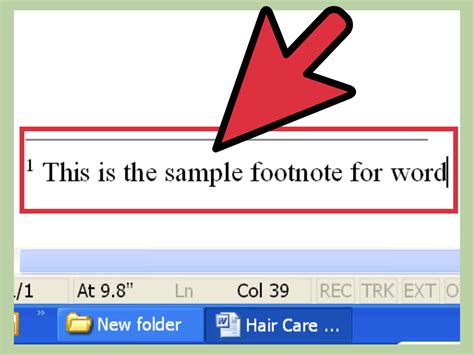
For researchers and writers who need to manage a large number of sources and citations, citation management tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley can be incredibly useful. These tools often include features for automatically formatting footnotes and bibliographies according to various citation styles (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.): - Import your sources into the citation management tool. - Use the tool’s plugin or integration with your word processor to insert citations and footnotes. - The tool will format your footnotes and bibliography according to your chosen citation style.
In summary, adding footnotes to your writing can be accomplished in several ways, each with its own advantages and suitable contexts. Whether you’re using word processing software, manually inserting footnotes, working with LaTeX, coding in HTML, or leveraging citation management tools, the key is to ensure that your footnotes are clear, concise, and provide valuable additional information to your readers. By mastering these methods, you can enhance the clarity and credibility of your writing, engaging your audience more effectively and contributing meaningfully to academic and public discourse.
What is the primary purpose of using footnotes in academic writing?
+
The primary purpose of using footnotes is to provide additional information, cite sources, and offer further context without disrupting the flow of the main text.
How do I decide which method to use for adding footnotes?

+
The choice of method depends on the context of your writing, the tools you are using, and your personal preference. For example, if you’re working on a web-based project, using HTML might be the most appropriate choice.
Can I use footnotes for creative writing?

+
While footnotes are more commonly associated with academic and non-fiction writing, they can also be used in creative writing to add depth, provide background information, or break the fourth wall, depending on the style and intent of the author.