Insert E in Excel
Inserting Data into Excel: A Comprehensive Guide
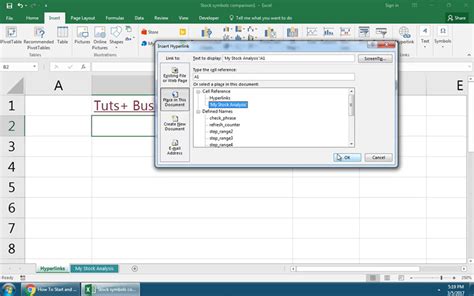
When working with Excel, one of the most fundamental tasks is inserting data into a spreadsheet. This can include anything from simple numbers and text to more complex data types like formulas and functions. In this guide, we will explore the various ways to insert data into Excel, including the use of the INSERT function, shortcuts, and other essential techniques.
Understanding the INSERT Function
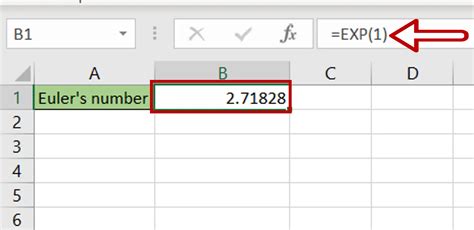
The INSERT function in Excel is a powerful tool that allows you to add new data to a spreadsheet. This can be done in several ways, including: * Using the INSERT button in the ribbon * Right-clicking on a cell and selecting Insert * Using the Ctrl + Shift + Plus Sign (+) shortcut
Inserting Cells, Rows, and Columns
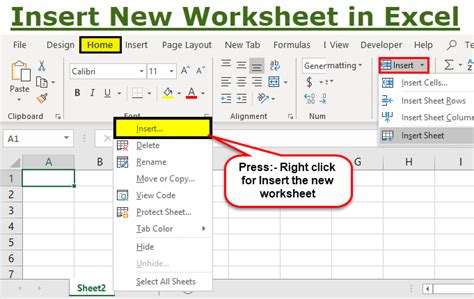
When working with Excel, it’s often necessary to insert new cells, rows, or columns to accommodate additional data. This can be done using the following methods: * To insert a new cell, select the cell below where you want to insert the new cell, and then use the INSERT button or right-click and select Insert. * To insert a new row, select the row below where you want to insert the new row, and then use the INSERT button or right-click and select Insert. * To insert a new column, select the column to the right of where you want to insert the new column, and then use the INSERT button or right-click and select Insert.
Using Shortcuts to Insert Data
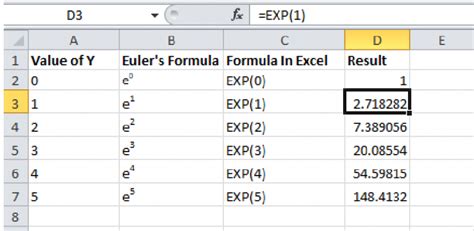
Excel provides several shortcuts that can make inserting data faster and more efficient. Some of the most useful shortcuts include: * Ctrl + Shift + Plus Sign (+) to insert a new cell, row, or column * Ctrl + C to copy a cell or range of cells * Ctrl + V to paste a cell or range of cells * Ctrl + Z to undo an action
Inserting Formulas and Functions

In addition to inserting simple data, Excel also allows you to insert formulas and functions. This can be done using the following methods: * Select the cell where you want to insert the formula or function * Type the formula or function using the = sign * Use the FORMULA tab in the ribbon to select from a list of available functions
Using Tables to Organize Data
Tables are a powerful tool in Excel that allow you to organize and analyze data more efficiently. To insert a table, follow these steps: * Select the range of cells that you want to convert to a table * Go to the INSERT tab in the ribbon * Click on the Table button * Follow the prompts to create the table
| Table Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Header Table | A table with headers in the first row |
| Footer Table | A table with footers in the last row |
| Total Table | A table with totals in the last row |
📝 Note: When working with tables, it's essential to use the TABLE tools in the ribbon to ensure that the table is formatted correctly.
To summarize, inserting data into Excel is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using a variety of methods, including the INSERT function, shortcuts, and tables. By mastering these techniques, you can become more efficient and effective in your work with Excel. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, understanding how to insert data into Excel is essential for getting the most out of this powerful spreadsheet software.
What is the purpose of the INSERT function in Excel?
+
The INSERT function in Excel is used to add new data to a spreadsheet, including cells, rows, and columns.
How do I insert a new row in Excel?

+
To insert a new row in Excel, select the row below where you want to insert the new row, and then use the INSERT button or right-click and select Insert.
What is the shortcut to insert a new cell in Excel?
+
The shortcut to insert a new cell in Excel is Ctrl + Shift + Plus Sign (+).
How do I create a table in Excel?
+
To create a table in Excel, select the range of cells that you want to convert to a table, go to the INSERT tab in the ribbon, click on the Table button, and follow the prompts to create the table.
What are the benefits of using tables in Excel?
+
The benefits of using tables in Excel include improved data organization, easier data analysis, and enhanced formatting options.