5 Ways To Graph
Introduction to Graphing
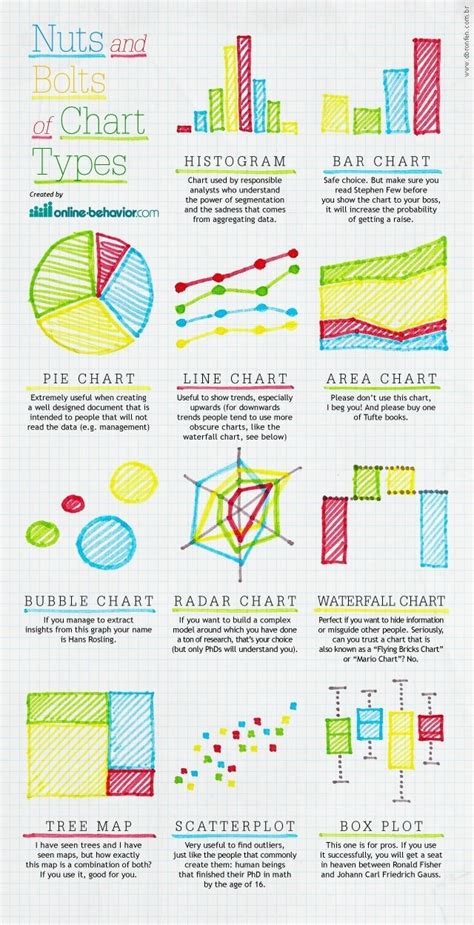
Graphing is a fundamental concept in mathematics and science, used to visualize and analyze relationships between variables. It is a powerful tool for understanding complex data, identifying patterns, and making predictions. In this article, we will explore five ways to graph, including line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms.
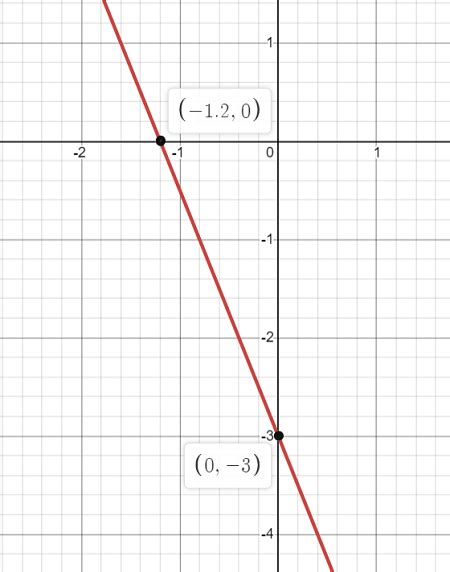
Line Graphs
Line graphs are used to display the relationship between two variables, typically with one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. They are particularly useful for showing trends over time or across different categories. To create a line graph, follow these steps: * Determine the variables to be graphed * Choose a scale for each axis * Plot the data points * Draw a line connecting the data points Some key considerations when creating line graphs include: * Using a clear and concise title * Labeling the axes correctly * Using a consistent scale
Bar Graphs
Bar graphs are used to compare the values of different categories. They consist of a series of bars, each representing a category, with the height of the bar corresponding to the value. Bar graphs can be used to display both nominal and ordinal data. To create a bar graph, follow these steps: * Determine the categories to be graphed * Choose a scale for the y-axis * Plot the data points * Draw bars to represent each category Some key considerations when creating bar graphs include: * Using a clear and concise title * Labeling the axes correctly * Using a consistent scale
Pie Charts
Pie charts are used to display the proportion of each category in a dataset. They consist of a circle divided into segments, each representing a category, with the size of the segment corresponding to the proportion. Pie charts are particularly useful for showing how different categories contribute to a whole. To create a pie chart, follow these steps: * Determine the categories to be graphed * Calculate the proportion of each category * Draw a circle to represent the whole * Divide the circle into segments to represent each category Some key considerations when creating pie charts include: * Using a clear and concise title * Labeling the segments correctly * Using a consistent scale
Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to display the relationship between two variables. They consist of a series of points, each representing a data point, with the x-coordinate corresponding to one variable and the y-coordinate corresponding to the other. Scatter plots are particularly useful for identifying patterns and correlations. To create a scatter plot, follow these steps: * Determine the variables to be graphed * Choose a scale for each axis * Plot the data points * Look for patterns and correlations Some key considerations when creating scatter plots include: * Using a clear and concise title * Labeling the axes correctly * Using a consistent scale
Histograms
Histograms are used to display the distribution of a single variable. They consist of a series of bars, each representing a range of values, with the height of the bar corresponding to the frequency. Histograms are particularly useful for showing the shape of a distribution. To create a histogram, follow these steps: * Determine the variable to be graphed * Choose a scale for the x-axis * Divide the data into ranges * Plot the frequency of each range Some key considerations when creating histograms include: * Using a clear and concise title * Labeling the axes correctly * Using a consistent scale
💡 Note: When creating graphs, it is essential to consider the audience and purpose of the graph. Different types of graphs are better suited for different types of data and different purposes.
In summary, graphing is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data. By choosing the right type of graph and following best practices for creation, you can effectively communicate insights and trends to your audience. Whether you are working with line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, or histograms, the key is to use a clear and concise title, label the axes correctly, and use a consistent scale. By doing so, you can create graphs that are both informative and engaging.
What is the purpose of graphing?
+
The purpose of graphing is to visualize and analyze relationships between variables, making it easier to understand complex data and identify patterns and trends.
What types of graphs are commonly used?
+
Commonly used types of graphs include line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms. Each type of graph is suited for different types of data and purposes.
How do I choose the right type of graph?
+
To choose the right type of graph, consider the type of data you are working with, the purpose of the graph, and the audience. Different types of graphs are better suited for different types of data and purposes.