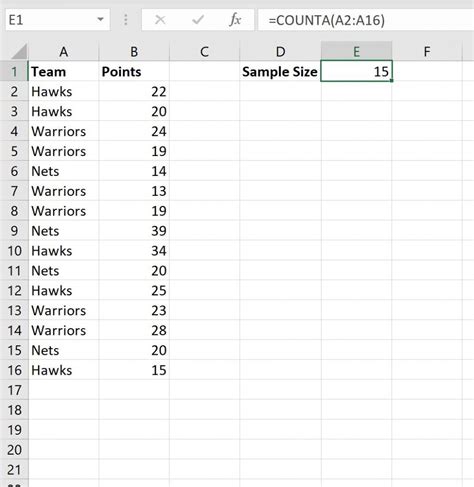
5 Ways To Find Sample Size
Introduction to Sample Size Calculation
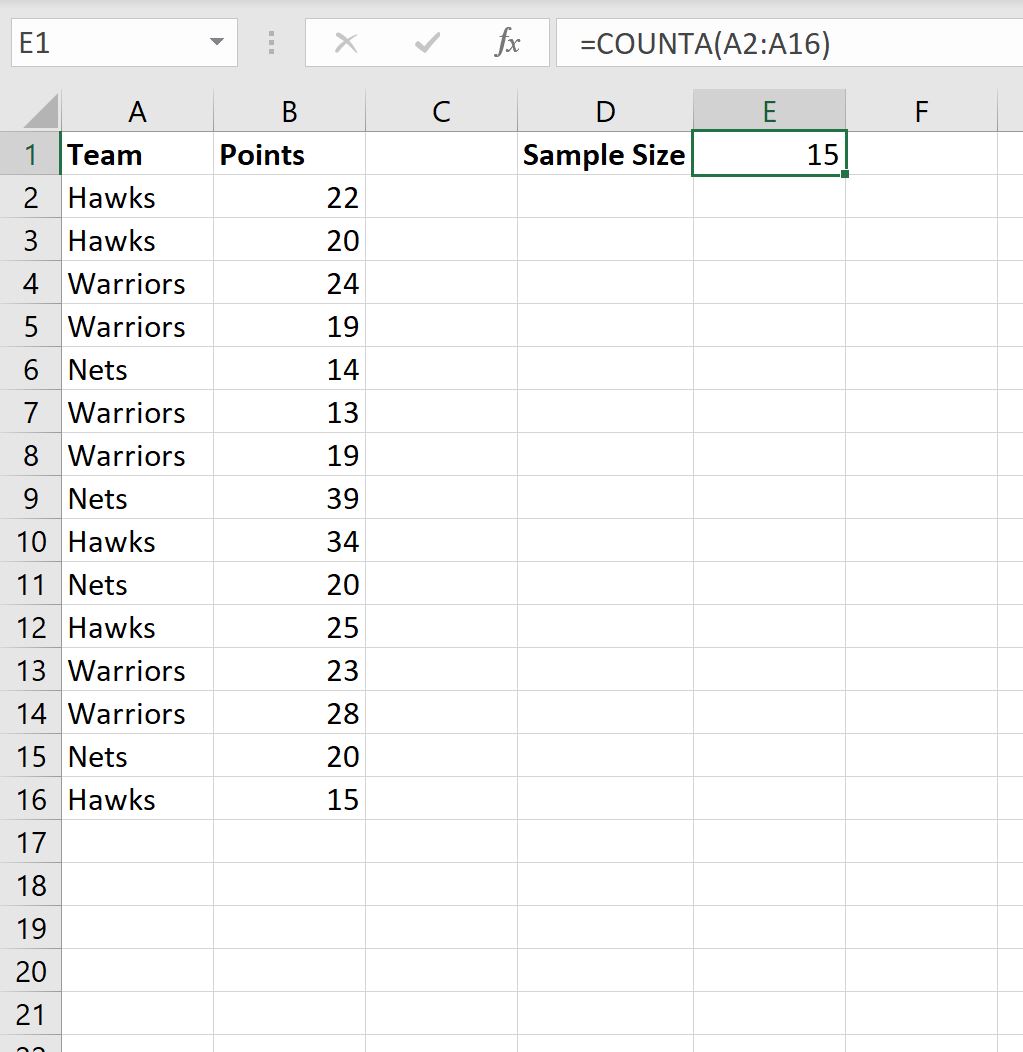
When conducting research or surveys, determining the appropriate sample size is crucial for ensuring the validity and reliability of the results. A sample size that is too small may not accurately represent the population, while a sample size that is too large can be costly and unnecessary. In this article, we will explore five ways to find sample size, including formulas, online calculators, and statistical software.
Understanding the Importance of Sample Size

Before diving into the methods for calculating sample size, it is essential to understand why sample size is critical in research. A sufficient sample size helps to: * Reduce sampling error, which occurs when the sample does not accurately represent the population * Increase statistical power, which is the ability to detect significant differences or relationships * Provide more precise estimates of population parameters
Method 1: Using Formulas to Calculate Sample Size

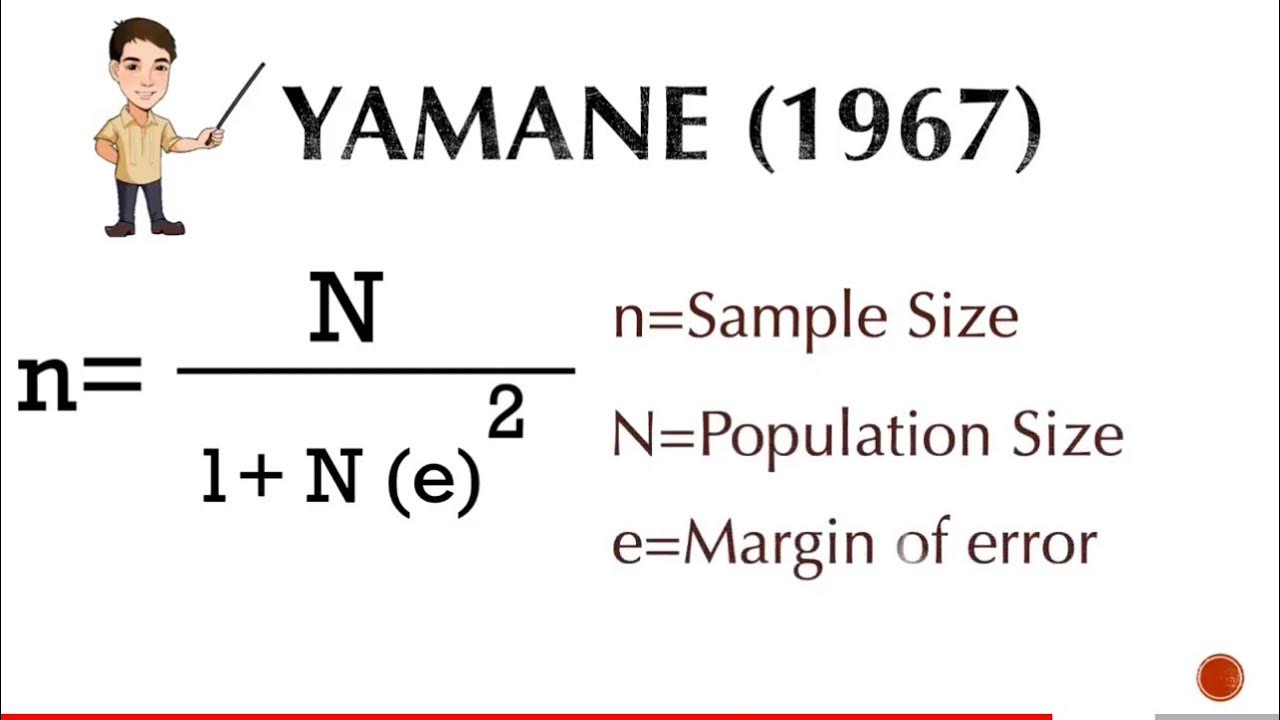
One way to calculate sample size is by using formulas, such as the Slovin’s formula: [ n = \frac{N}{1 + Ne^2} ] where: * n = sample size * N = population size * e = margin of error This formula provides a rough estimate of the sample size required to achieve a specified margin of error.
Method 2: Utilizing Online Calculators
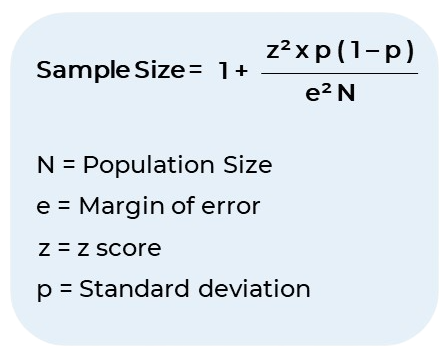
Another way to calculate sample size is by using online calculators, such as those found on websites like SurveyMonkey or Stat Trek. These calculators often require input of the following parameters: * Population size * Margin of error * Confidence level * Expected response rate (for surveys) Using online calculators can save time and reduce errors associated with manual calculations.
Method 3: Employing Statistical Software
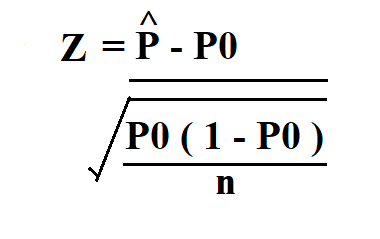
Statistical software, such as R or SPSS, can also be used to calculate sample size. These programs often have built-in functions or modules specifically designed for sample size calculation. For example, in R, the samplesize package provides functions for calculating sample size for various study designs.
Method 4: Consulting Sample Size Tables

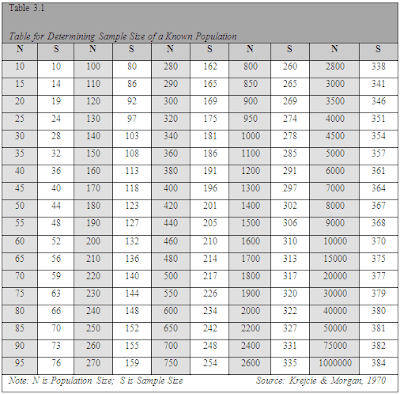
Sample size tables, such as those found in statistical textbooks or online resources, provide pre-calculated sample sizes for different scenarios. These tables often list the required sample size based on factors like: * Population size * Margin of error * Confidence level * Type of study design (e.g., survey, experiment) Using sample size tables can be a quick and easy way to estimate the required sample size.
Method 5: Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms, such as random forest or support vector machines, can be used to predict the required sample size based on historical data or similar studies. This approach can be particularly useful when dealing with complex datasets or multiple variables.
📝 Note: When using machine learning algorithms, it is essential to validate the results using traditional sample size calculation methods to ensure accuracy.
Summary of Methods
In summary, there are various ways to calculate sample size, including: * Using formulas, such as Slovin’s formula * Utilizing online calculators * Employing statistical software * Consulting sample size tables * Using machine learning algorithms Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific research question, study design, and available resources.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Formulas | Simple, quick, and easy to use | May not account for all variables, can be inaccurate |
| Online Calculators | Convenient, fast, and accurate | May require input of multiple parameters, can be limited in scope |
| Statistical Software | Flexible, powerful, and accurate | Can be complex, requires expertise, and may be costly |
| Sample Size Tables | Quick, easy, and convenient | May not account for all variables, can be limited in scope |
| Machine Learning Algorithms | Can handle complex datasets, accurate, and efficient | Requires expertise, can be computationally intensive, and may require large datasets |
In conclusion, determining the appropriate sample size is a critical step in research and survey design. By understanding the various methods for calculating sample size, researchers can ensure that their studies are adequately powered and provide reliable results. Whether using formulas, online calculators, statistical software, sample size tables, or machine learning algorithms, the key is to select the method that best suits the research question and available resources.
What is the minimum sample size required for a survey?
+
The minimum sample size required for a survey depends on the population size, margin of error, and confidence level. A common rule of thumb is to use a sample size of at least 30, but this can vary depending on the specific research question and study design.
How do I calculate sample size for a regression analysis?

+
To calculate sample size for a regression analysis, you can use the following formula: n = (Z^2 * σ^2) / E^2, where n is the sample size, Z is the Z-score, σ is the standard deviation, and E is the margin of error. Alternatively, you can use online calculators or statistical software to determine the required sample size.
Can I use machine learning algorithms to predict sample size for any type of study?
+
Machine learning algorithms can be used to predict sample size for various types of studies, but they are not suitable for all scenarios. For example, machine learning algorithms may not be effective for small population sizes or studies with complex designs. It is essential to evaluate the suitability of machine learning algorithms for your specific research question and study design.