5 Ways To Measure P Value

Introduction to P-Value Measurement

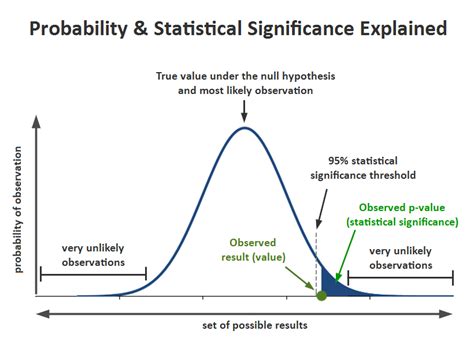
The p-value is a crucial concept in statistical hypothesis testing, representing the probability of observing results at least as extreme as those observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. It is a fundamental measure used to determine the significance of the results obtained from a statistical test. In this blog post, we will explore five ways to measure the p-value and understand its importance in statistical analysis.
Understanding P-Value
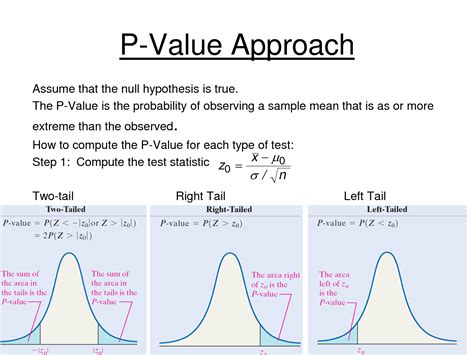
Before diving into the methods of measuring the p-value, it’s essential to understand what it represents. The p-value is a numerical value between 0 and 1, where: - A p-value close to 0 indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis. - A p-value close to 1 indicates weak evidence against the null hypothesis. The p-value is often compared to a significance level, usually denoted as α (alpha), which is set before the test. If the p-value is less than α, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Methods to Measure P-Value
Here are five common methods used to measure the p-value:
- Z-Test: This method is used for large sample sizes and is based on the standard normal distribution. The p-value is calculated using the Z-score, which measures how many standard deviations an element is from the mean.
- T-Test: This method is used for small sample sizes and is based on the t-distribution. The p-value is calculated using the t-score, which is similar to the Z-score but takes into account the sample size.
- Chi-Squared Test: This method is used for categorical data and is based on the chi-squared distribution. The p-value is calculated using the chi-squared statistic, which measures the difference between observed and expected frequencies.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): This method is used to compare means of three or more samples and is based on the F-distribution. The p-value is calculated using the F-statistic, which measures the ratio of variance between groups to variance within groups.
- Non-Parametric Tests: These methods are used when the data does not meet the assumptions of parametric tests, such as normality or equal variances. Examples of non-parametric tests include the Wilcoxon rank-sum test and the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Interpretation of P-Value

Interpreting the p-value is crucial in understanding the results of a statistical test. Here are some key points to consider: - A small p-value (α) indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis. - A large p-value (> α) indicates weak evidence against the null hypothesis. - The p-value does not indicate the probability of the null hypothesis being true or false. - The p-value is sensitive to sample size, and large samples can result in statistically significant results even if the effect size is small.
📝 Note: It's essential to consider the research question, study design, and data analysis when interpreting the p-value, as it's only one aspect of the results.
Common Mistakes in P-Value Interpretation
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when interpreting the p-value: * Misinterpreting the p-value as the probability of the null hypothesis being true: The p-value does not provide information about the probability of the null hypothesis being true or false. * Overemphasizing the importance of statistical significance: Statistical significance does not necessarily imply practical significance. * Ignoring the effect size: The p-value only indicates whether the results are statistically significant, but not the magnitude of the effect.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Z-Test | Used for large sample sizes, based on standard normal distribution |
| T-Test | Used for small sample sizes, based on t-distribution |
| Chi-Squared Test | Used for categorical data, based on chi-squared distribution |
| ANOVA | Used to compare means of three or more samples, based on F-distribution |
| Non-Parametric Tests | Used when data does not meet assumptions of parametric tests |
In summary, the p-value is a crucial measure in statistical hypothesis testing, and understanding its interpretation is essential in drawing conclusions from research findings. By considering the research question, study design, and data analysis, and avoiding common mistakes in interpretation, researchers can make informed decisions based on the results of their studies. The five methods outlined in this post provide a range of options for measuring the p-value, each with its own strengths and limitations.
What is the p-value?
+
The p-value is a numerical value between 0 and 1 that represents the probability of observing results at least as extreme as those observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
How is the p-value interpreted?
+
A small p-value (less than the significance level) indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, while a large p-value (greater than the significance level) indicates weak evidence against the null hypothesis.
What are the common mistakes in p-value interpretation?

+
Common mistakes include misinterpreting the p-value as the probability of the null hypothesis being true, overemphasizing the importance of statistical significance, and ignoring the effect size.