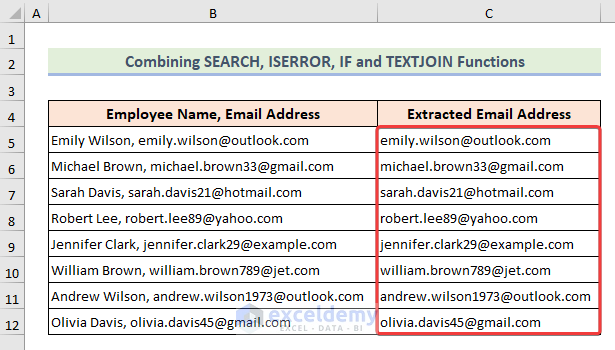
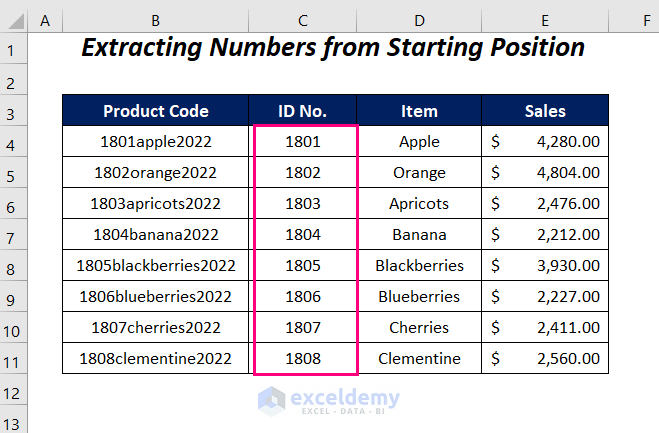
5 Ways Extract Cell Data
Introduction to Extracting Cell Data
Extracting cell data is a crucial step in various scientific and research applications, including biology, medicine, and biotechnology. Cell data extraction involves obtaining specific information from cells, such as genetic material, proteins, or other biomolecules. In this article, we will discuss five ways to extract cell data, highlighting the advantages and limitations of each method.
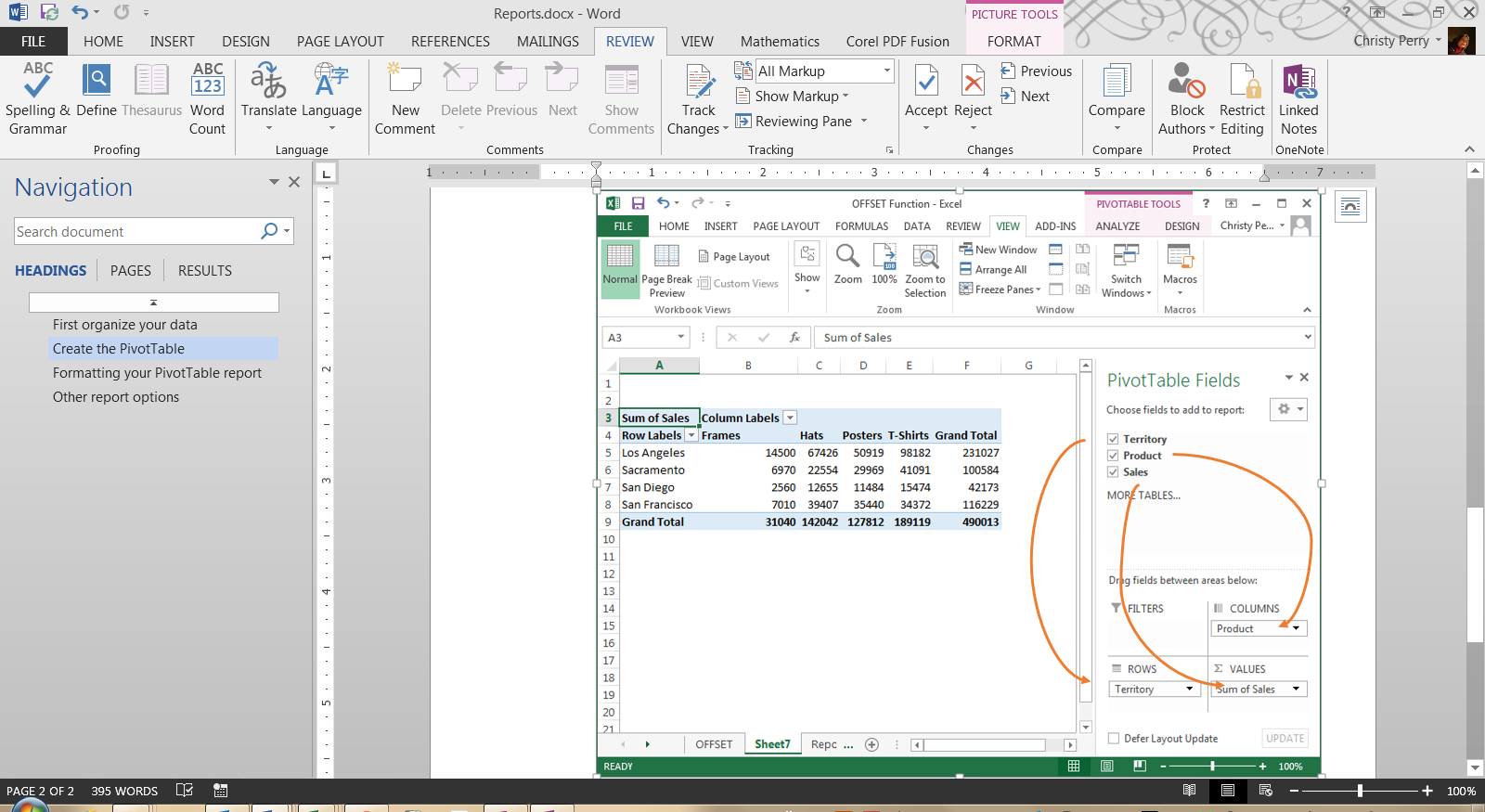
1. Microdissection
Microdissection is a technique used to extract specific cells or cell components from a tissue sample. This method involves using a microscope and a precision instrument, such as a laser or a needle, to dissect and collect individual cells or cell clusters. Microdissection is particularly useful for analyzing specific cell populations, such as cancer cells, and for studying cell-to-cell interactions. The advantages of microdissection include its high precision and the ability to analyze specific cell populations. However, this method can be time-consuming and requires specialized equipment and expertise.
2. Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique used to analyze and sort cells based on their physical and chemical properties, such as size, shape, and fluorescence. This method involves suspending cells in a fluid and passing them through a laser beam, which excites fluorescent dyes attached to specific cell surface markers. The resulting fluorescence signals are then detected and analyzed using specialized software. Flow cytometry is widely used in immunology, cancer research, and stem cell biology. The advantages of flow cytometry include its high throughput and the ability to analyze multiple cell populations simultaneously. However, this method requires specialized equipment and can be affected by cell viability and sample preparation.
3. Cell Sorting

Cell sorting is a technique used to separate and purify specific cell populations based on their physical and chemical properties. This method involves using a combination of flow cytometry and sorting instruments, such as fluorescence-activated cell sorters (FACS), to isolate specific cell populations. Cell sorting is widely used in research and clinical applications, including immunology, cancer research, and regenerative medicine. The advantages of cell sorting include its high precision and the ability to obtain pure cell populations. However, this method can be time-consuming and requires specialized equipment and expertise.
4. Magnetic Bead Separation

Magnetic bead separation is a technique used to isolate specific cell populations based on their surface markers. This method involves attaching magnetic beads to specific cell surface markers and then separating the cells using a magnetic field. Magnetic bead separation is widely used in research and clinical applications, including immunology, cancer research, and stem cell biology. The advantages of magnetic bead separation include its simplicity and the ability to isolate specific cell populations quickly and efficiently. However, this method can be affected by cell viability and sample preparation.
5. Laser Capture Microdissection

Laser capture microdissection (LCM) is a technique used to extract specific cells or cell components from a tissue sample. This method involves using a laser to cut out specific cells or cell clusters and then capturing them using a specialized instrument. LCM is widely used in research and clinical applications, including cancer research, neuroscience, and genetics. The advantages of LCM include its high precision and the ability to analyze specific cell populations. However, this method can be time-consuming and requires specialized equipment and expertise.
💡 Note: The choice of method for extracting cell data depends on the specific research question, the type of cells being studied, and the available equipment and expertise.
In summary, extracting cell data is a crucial step in various scientific and research applications. The five methods discussed in this article, including microdissection, flow cytometry, cell sorting, magnetic bead separation, and laser capture microdissection, offer different advantages and limitations. By choosing the most suitable method, researchers can obtain high-quality cell data and advance our understanding of cellular biology and disease mechanisms.
What is the most commonly used method for extracting cell data?
+
Flow cytometry is one of the most commonly used methods for extracting cell data, particularly in immunology and cancer research.
What are the advantages of microdissection?
+
Microdissection offers high precision and the ability to analyze specific cell populations, making it a valuable tool for studying cell-to-cell interactions and specific cell populations.
Can magnetic bead separation be used for clinical applications?

+
Yes, magnetic bead separation can be used for clinical applications, including immunology and cancer research, to isolate specific cell populations for further analysis or treatment.