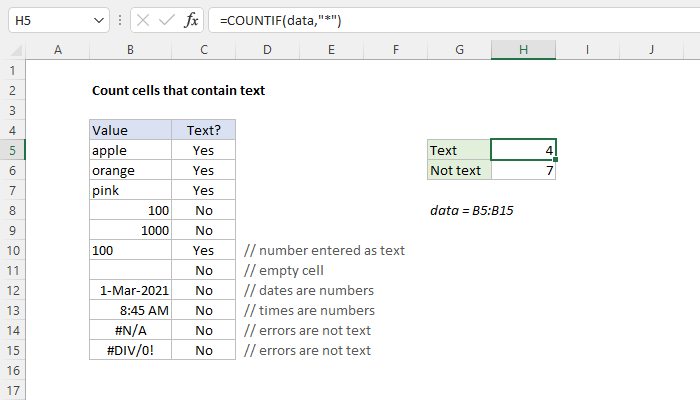
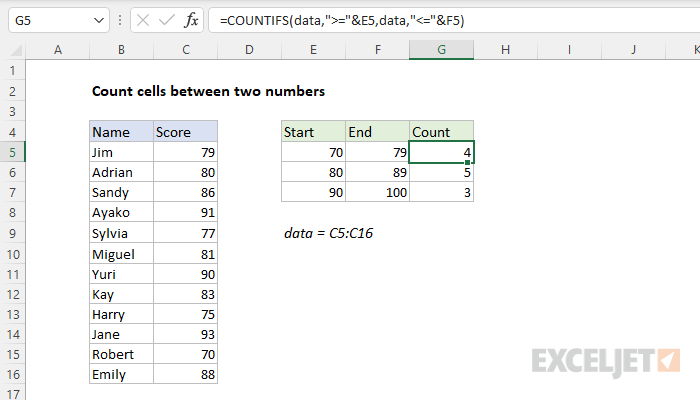
5 Ways Count Cells
Introduction to Counting Cells
Counting cells is a fundamental technique in various fields, including biology, medicine, and research. It involves determining the number of cells in a sample, which can be crucial for understanding cellular behavior, diagnosing diseases, and developing new treatments. There are several methods to count cells, each with its advantages and limitations. In this article, we will explore five ways to count cells, highlighting their principles, applications, and considerations.
1. Manual Counting using a Hemocytometer
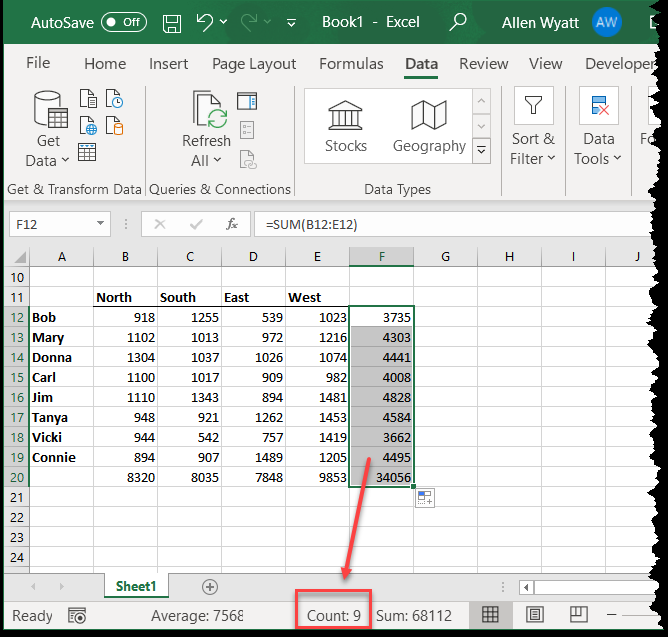
Manual counting using a hemocytometer is a traditional and straightforward method for counting cells. A hemocytometer is a specialized microscope slide with a grid etched onto its surface, allowing for the precise counting of cells within a defined area. To perform manual counting, a sample of cells is diluted to an appropriate concentration, and a small volume is placed onto the hemocytometer. The cells are then counted visually using a microscope, and the total number of cells is calculated based on the dilution factor and the volume of the sample. Manual counting is a simple and cost-effective method but can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
2. Automated Cell Counting using Image Analysis Software
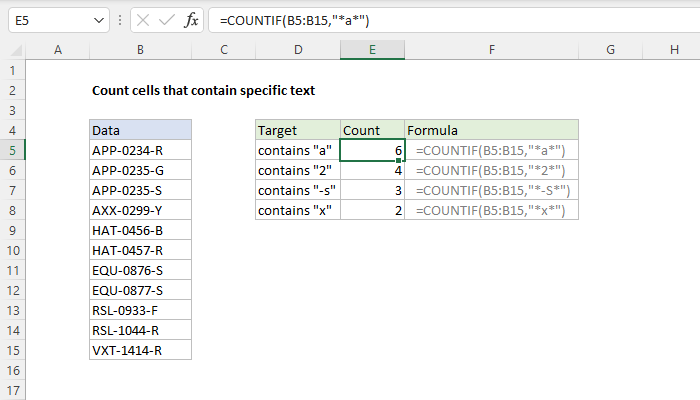
Automated cell counting using image analysis software is a more efficient and accurate method compared to manual counting. This approach involves capturing images of the cells using a microscope or a camera and then analyzing the images using specialized software. The software can detect and count cells based on their size, shape, and intensity, reducing the risk of human error. Automated cell counting is particularly useful for large-scale cell counting and can be integrated with high-throughput screening applications. However, the accuracy of automated counting depends on the quality of the images and the algorithms used for cell detection.
3. Flow Cytometry

Flow cytometry is a powerful technique for counting and analyzing cells based on their physical and chemical properties. This method involves suspending cells in a fluid stream and passing them through a laser beam, which scatters light as the cells pass through. The scattered light is then detected and analyzed to determine the size, shape, and granularity of the cells. Flow cytometry can also be used to detect specific markers or proteins on the surface of cells, allowing for the identification and counting of specific cell populations. Flow cytometry is widely used in research and clinical applications, including immunology, cancer diagnosis, and stem cell biology.
4. Spectrophotometry

Spectrophotometry is a method for counting cells based on their absorbance or transmittance of light. This approach involves measuring the optical density of a cell suspension at a specific wavelength, which is directly proportional to the number of cells present. Spectrophotometry is a rapid and non-invasive method for estimating cell density and can be used to monitor cell growth and proliferation. However, spectrophotometry may not be as accurate as other methods, especially for cells with variable sizes or shapes.
5. Electrochemical Cell Counting

Electrochemical cell counting is a novel method that uses electrochemical signals to detect and count cells. This approach involves measuring the changes in electrical impedance or conductivity caused by the presence of cells in a solution. Electrochemical cell counting is a label-free and non-invasive method that can be used to count cells in real-time, making it suitable for monitoring cell growth and behavior in various applications, including biotechnology and biomedical research.
📝 Note: The choice of cell counting method depends on the specific application, cell type, and desired level of accuracy. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and it is essential to consider these factors when selecting a cell counting technique.
To summarize, counting cells is a critical step in various fields, and several methods are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the principles and applications of these methods, researchers and scientists can choose the most suitable approach for their specific needs and accurately determine the number of cells in their samples.
What is the most accurate method for counting cells?
+
The most accurate method for counting cells depends on the specific application and cell type. However, flow cytometry is generally considered one of the most accurate methods, as it can detect and count cells based on their physical and chemical properties.
What are the advantages of automated cell counting?
+
Automated cell counting offers several advantages, including increased speed, accuracy, and reproducibility. It can also reduce the risk of human error and is particularly useful for large-scale cell counting applications.
Can spectrophotometry be used to count cells in real-time?
+
Yes, spectrophotometry can be used to estimate cell density in real-time. However, its accuracy may be affected by various factors, such as cell size, shape, and aggregation.