5 Ways Calculate P Value
Introduction to P-Value Calculation

The P-value, or probability value, is a key concept in statistical hypothesis testing, representing the probability of observing results at least as extreme as those observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. Calculating the P-value is crucial in determining whether the results of a study are statistically significant. There are several methods to calculate the P-value, depending on the type of data and the nature of the hypothesis being tested. In this article, we will explore five common ways to calculate the P-value.
Understanding the Basics of P-Value
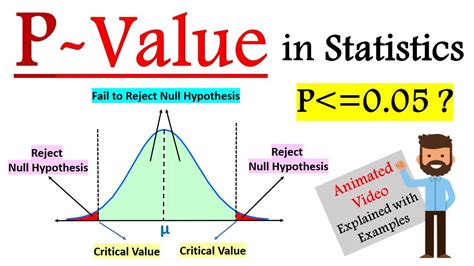
Before diving into the calculation methods, it’s essential to understand what the P-value represents. The P-value is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the strength of evidence against a null hypothesis. A small P-value (typically less than 0.05) suggests that the observed data would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
1. Using the Z-Test for P-Value Calculation
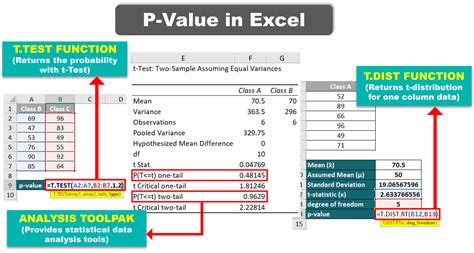
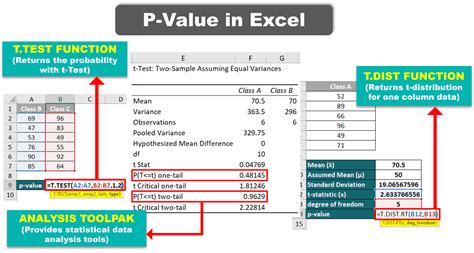
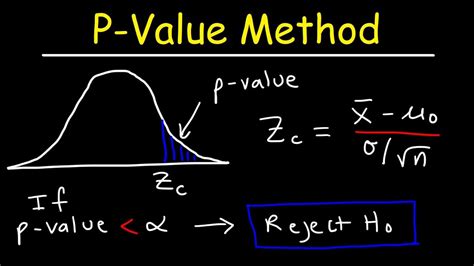
The Z-test is used for comparing the mean of a sample to a known population mean or for comparing the means of two samples, assuming that the population variances are known. The formula for calculating the Z-score is: [ Z = \frac{(\bar{X} - \mu)}{\sigma / \sqrt{n}} ] where (\bar{X}) is the sample mean, (\mu) is the population mean, (\sigma) is the population standard deviation, and (n) is the sample size. The P-value can then be found using a Z-table or a statistical calculator, looking up the Z-score to find the corresponding probability.
2. T-Test for P-Value Calculation
The T-test is similar to the Z-test but is used when the population variance is unknown. There are three types of T-tests: the one-sample T-test, the independent samples T-test, and the paired samples T-test. The formula for the T-score in a one-sample T-test is: [ T = \frac{(\bar{X} - \mu)}{s / \sqrt{n}} ] where (s) is the sample standard deviation. The P-value is determined by looking up the T-score in a T-distribution table, with the degrees of freedom being (n-1).
3. ANOVA for Multiple Group Comparisons

Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is used to compare means among three or more groups. The P-value in ANOVA is calculated based on the F-statistic, which compares the variance between groups to the variance within groups. The formula for the F-statistic is: [ F = \frac{MS{between}}{MS{within}} ] where (MS{between}) is the mean square between groups and (MS{within}) is the mean square within groups. The P-value is then found using an F-distribution table with the appropriate degrees of freedom.
4. Chi-Square Test for Categorical Data
The Chi-Square test is used for categorical data to determine if there is a significant association between two variables. The Chi-Square statistic is calculated as: [ \chi^2 = \sum \frac{(observed - expected)^2}{expected} ] The P-value is found by looking up the Chi-Square statistic in a Chi-Square distribution table, with the degrees of freedom being ((r-1)(c-1)) for an (r \times c) contingency table.
5. Non-Parametric Tests

Non-parametric tests are used when the data does not meet the assumptions of parametric tests, such as normality or equal variances. Examples include the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (for comparing two independent groups) and the Kruskal-Wallis test (for comparing more than two independent groups). The P-value for these tests can often be calculated using statistical software, as the formulas can be complex and involve permutations or rankings of the data.
📝 Note: The choice of test and the method of calculating the P-value depend on the research question, the type of data, and the assumptions that can be made about the data distribution.
To summarize, calculating the P-value is a critical step in statistical hypothesis testing, and the method of calculation depends on the nature of the data and the research question. Understanding how to calculate and interpret P-values is essential for making informed decisions based on statistical analysis.
What is the purpose of calculating the P-value in statistical analysis?
+
The purpose of calculating the P-value is to determine the statistical significance of the results, indicating whether the observed effects are likely due to chance or if they reflect a real phenomenon.
How do I choose the correct statistical test for calculating the P-value?
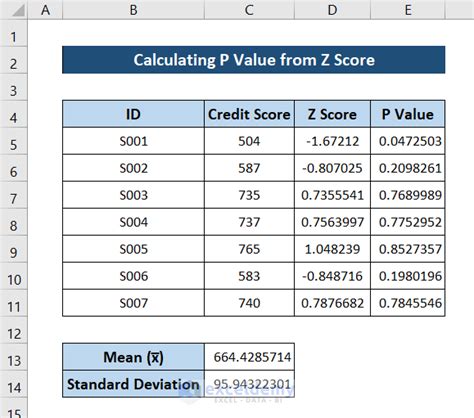
+
The choice of test depends on the type of data (continuous, categorical), the number of groups being compared, and the assumptions that can be made about the data distribution (e.g., normality, equal variances). Consulting with a statistician or using statistical software can help in selecting the appropriate test.
What is the difference between a significant and a non-significant P-value?

+
A significant P-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that the observed data would be unlikely under the null hypothesis, suggesting that the null hypothesis can be rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. A non-significant P-value indicates that the data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis, suggesting that the observed effects could be due to chance.