5 Ways Calculate Frequency
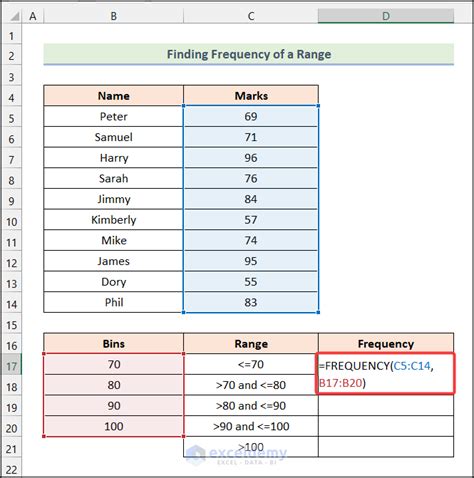
Understanding Frequency Calculation
Calculating frequency is a crucial aspect of various fields, including physics, engineering, and data analysis. Frequency refers to the number of occurrences or cycles per second of a repeating event, such as a wave or a signal. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate frequency, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying concepts and formulas.
1. Using the Formula: Frequency = 1 / Time Period

One of the most straightforward methods to calculate frequency is by using the formula: Frequency (f) = 1 / Time Period (T). This formula is applicable when the time period of the repeating event is known. For example, if the time period of a wave is 0.5 seconds, the frequency can be calculated as: f = 1 / 0.5 = 2 Hz. This method is widely used in physics and engineering to calculate the frequency of waves, signals, and other periodic phenomena.
2. Using the Formula: Frequency = Number of Cycles / Time
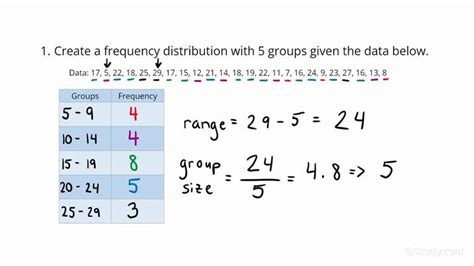
Another way to calculate frequency is by using the formula: Frequency (f) = Number of Cycles (n) / Time (t). This formula is useful when the number of cycles and the time are known. For instance, if a signal completes 10 cycles in 2 seconds, the frequency can be calculated as: f = 10 / 2 = 5 Hz. This method is commonly used in data analysis and signal processing to calculate the frequency of signals and patterns.
3. Using a Frequency Counter

A frequency counter is an electronic device that measures the frequency of a signal or a wave. This method is widely used in laboratories and industries to measure the frequency of signals and waves. The frequency counter works by counting the number of cycles of the signal or wave over a fixed time period, usually one second. The result is then displayed as the frequency of the signal or wave.
4. Using a Spectrometer
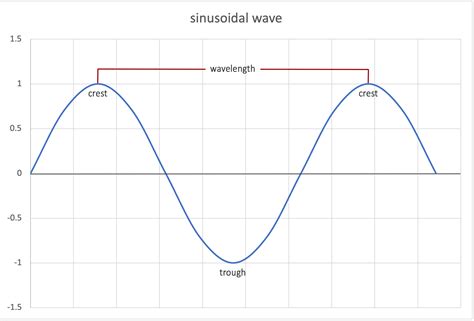
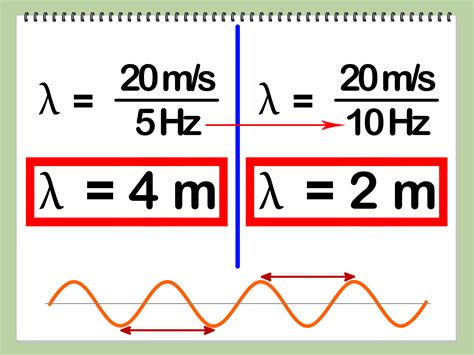
A spectrometer is an instrument that measures the distribution of light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Spectrometers can be used to calculate the frequency of light or other forms of radiation by measuring the wavelength and using the formula: Frequency (f) = Speed of Light © / Wavelength (λ). This method is commonly used in chemistry and physics to analyze the properties of materials and substances.
5. Using Software and Apps
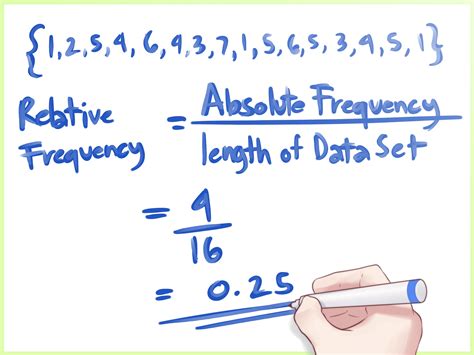
With the advancement of technology, there are now various software and apps available that can calculate frequency. These tools use algorithms and formulas to calculate the frequency of signals, waves, and other periodic phenomena. Some popular software and apps include MATLAB, Python, and FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) apps. These tools are widely used in data analysis, signal processing, and scientific research to calculate the frequency of complex signals and patterns.
📝 Note: When calculating frequency, it is essential to ensure that the units are consistent, and the formulas are applied correctly to avoid errors and inaccuracies.
To summarize, calculating frequency is a crucial aspect of various fields, and there are multiple methods to do so. The choice of method depends on the specific application, the availability of data, and the desired level of accuracy. By understanding the underlying concepts and formulas, individuals can apply these methods to calculate frequency and gain insights into the properties and behavior of various phenomena.
What is the unit of frequency?
+
The unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz), which represents the number of cycles per second.
How is frequency related to wavelength?

+
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional, as shown by the formula: Frequency (f) = Speed of Light © / Wavelength (λ).
What are some common applications of frequency calculation?
+
Frequency calculation has various applications in physics, engineering, data analysis, and signal processing, including the analysis of waves, signals, and periodic phenomena.