5 Ways Create Control Chart
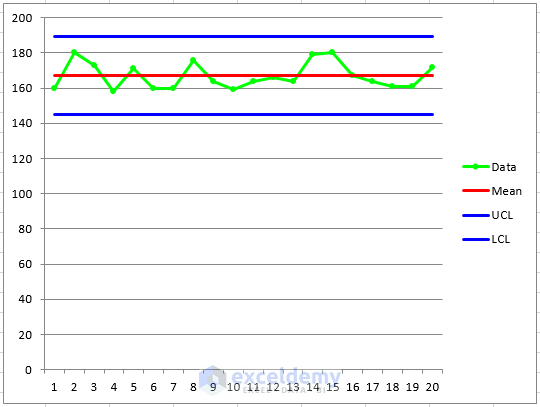
Introduction to Control Charts

Control charts are a powerful tool used in statistical process control to monitor and control processes. They help in detecting any shifts or trends in the process, allowing for corrective actions to be taken. Control charts can be used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. In this article, we will discuss the different types of control charts and provide a step-by-step guide on how to create them.
Types of Control Charts
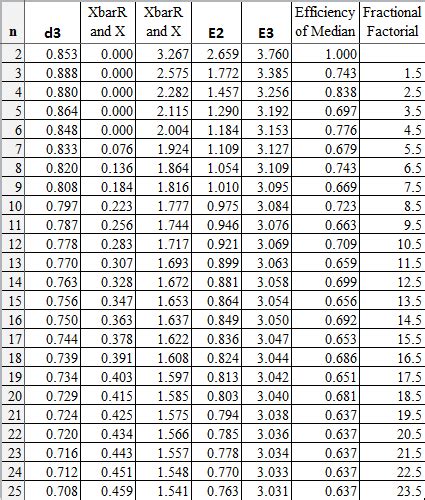
There are several types of control charts, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of control charts include: * X-bar chart: used to monitor the mean of a process * R-chart: used to monitor the range of a process * P-chart: used to monitor the proportion of defective items * NP-chart: used to monitor the number of defective items * U-chart: used to monitor the average number of defects per unit
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Control Chart
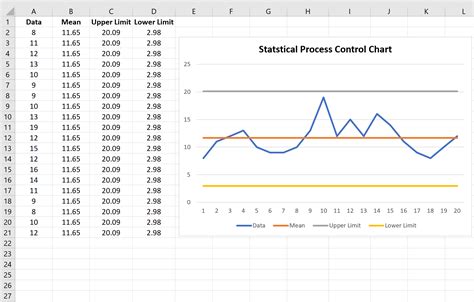
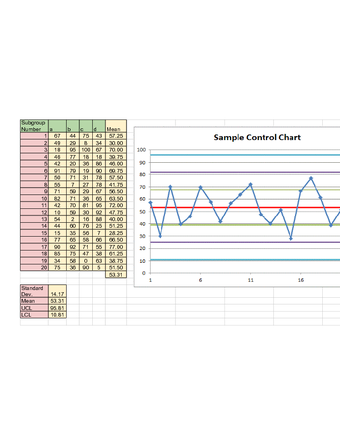
Creating a control chart involves several steps, including: * Collecting data: the first step is to collect data on the process being monitored. This can be done using random sampling or systematic sampling. * Calculating the mean and standard deviation: once the data has been collected, the next step is to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the process. * Determining the control limits: the control limits are the upper control limit (UCL) and the lower control limit (LCL). These limits are calculated using the mean and standard deviation of the process. * Plotting the data: the final step is to plot the data on the control chart. This involves plotting the individual data points on the chart, as well as the control limits.
5 Ways to Create a Control Chart
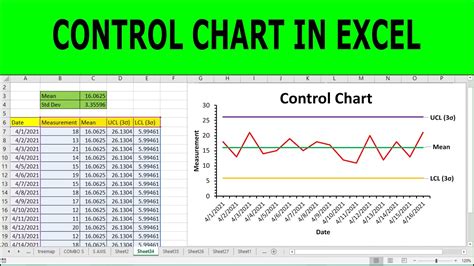
Here are 5 ways to create a control chart: * Manual calculation: this involves calculating the mean and standard deviation of the process manually, and then plotting the data on the control chart. * Using a spreadsheet: this involves using a spreadsheet program, such as Microsoft Excel, to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the process, and then plotting the data on the control chart. * Using specialized software: there are several specialized software programs available that can be used to create control charts, including Minitab and JMP. * Using a statistical process control (SPC) software: there are several SPC software programs available that can be used to create control charts, including Quality Window and SPC XL. * Using a programming language: this involves using a programming language, such as Python or R, to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the process, and then plotting the data on the control chart.
💡 Note: When creating a control chart, it is essential to ensure that the data is normally distributed and that the process is in control.
Example of a Control Chart
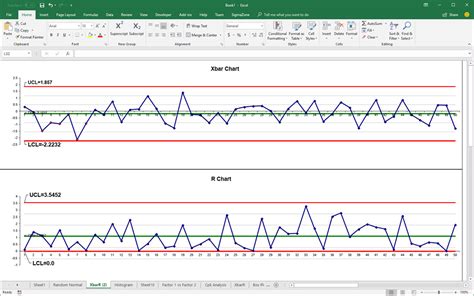
Here is an example of a control chart:
| Sample Number | Mean | Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.2 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 10.5 | 2.3 |
| 3 | 10.1 | 2.2 |
| 4 | 10.8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 10.3 | 2.4 |
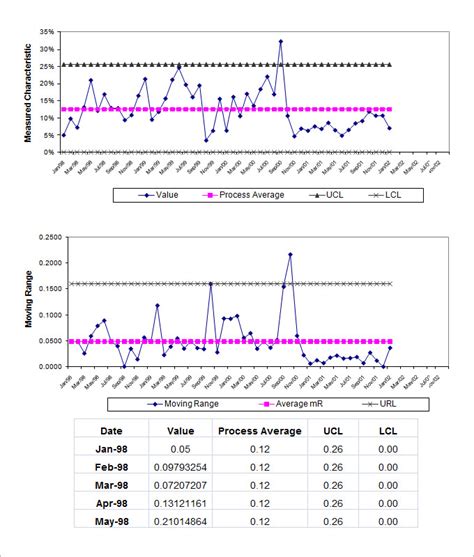
The control limits for this example are: * UCL: 11.2 * LCL: 9.8
Interpretation of Control Charts
Interpreting control charts involves analyzing the data to determine if the process is in control or out of control. If the process is in control, the data points will be randomly distributed within the control limits. If the process is out of control, the data points will be trending or shifted outside of the control limits.
In summary, control charts are a powerful tool used in statistical process control to monitor and control processes. There are several types of control charts, including X-bar charts, R-charts, P-charts, NP-charts, and U-charts. Creating a control chart involves several steps, including collecting data, calculating the mean and standard deviation, determining the control limits, and plotting the data. There are 5 ways to create a control chart, including manual calculation, using a spreadsheet, using specialized software, using a statistical process control (SPC) software, and using a programming language.
What is the purpose of a control chart?
+
The purpose of a control chart is to monitor and control processes, detecting any shifts or trends in the process, and allowing for corrective actions to be taken.
What are the different types of control charts?
+
There are several types of control charts, including X-bar charts, R-charts, P-charts, NP-charts, and U-charts.
How do I create a control chart?
+
To create a control chart, you need to collect data, calculate the mean and standard deviation, determine the control limits, and plot the data.
Related Terms:
- Control Chart in Excel template
- Control chart constants Excel
- Control chart example in Excel
- Control chart maker
- SPC chart Excel
- Control chart quality tool