Excel
5 Ways Excel Box Plot
Introduction to Excel Box Plot
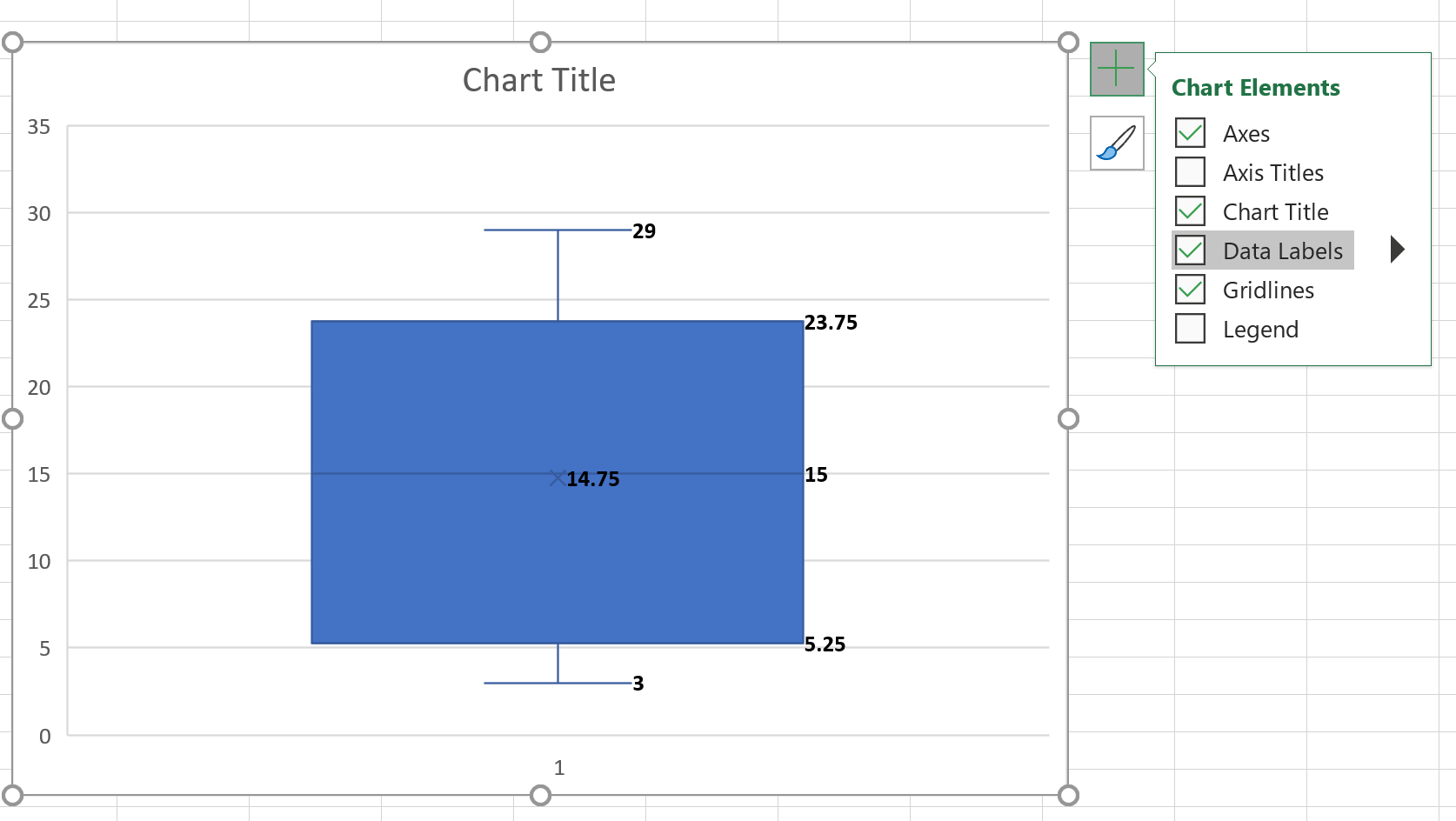
Excel box plot, also known as box and whisker plot, is a graphical representation used to display the distribution of data. It is a useful tool to visualize the median, quartiles, and outliers in a dataset. In this article, we will explore 5 ways to create and use Excel box plots to analyze and understand data.
What is a Box Plot?

A box plot is a graphical representation that displays the distribution of data through five key values: * Minimum: The smallest value in the dataset. * First quartile (Q1): The value below which 25% of the data falls. * Median (Q2): The middle value of the dataset. * Third quartile (Q3): The value below which 75% of the data falls. * Maximum: The largest value in the dataset. The box plot also shows outliers, which are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data.
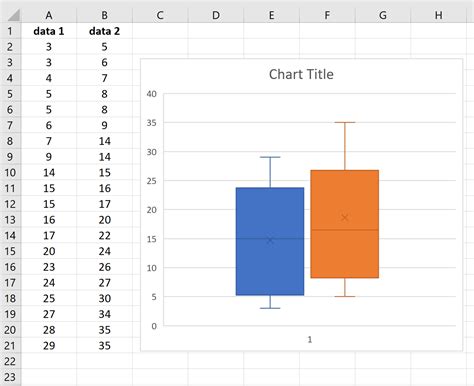
Creating a Box Plot in Excel

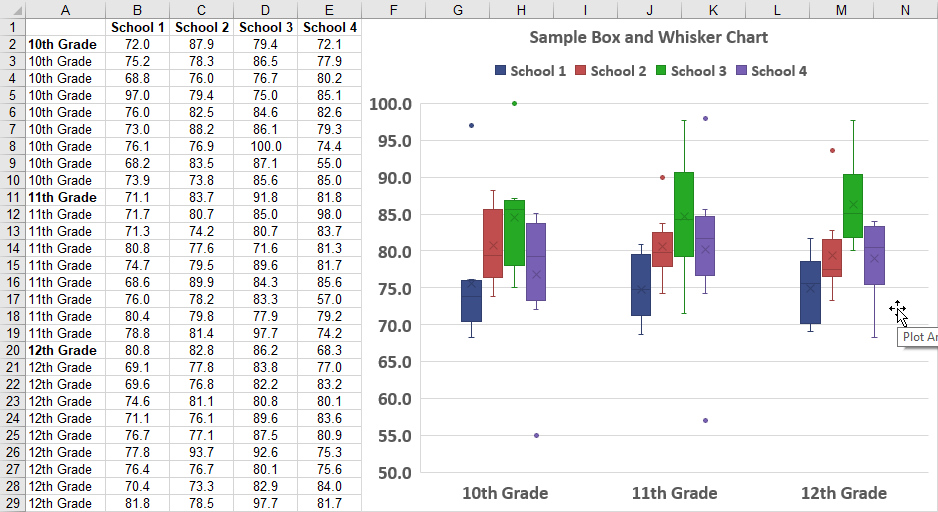
To create a box plot in Excel, follow these steps: * Select the data range that you want to analyze. * Go to the “Insert” tab in the ribbon. * Click on “Insert Statistic Chart” and select “Box and Whisker” chart. * Customize the chart as needed.
📊 Note: Make sure to select the correct data range and adjust the chart settings to get a clear and accurate representation of the data.
5 Ways to Use Excel Box Plot
Here are 5 ways to use Excel box plots to analyze and understand data: * Comparing distributions: Use box plots to compare the distribution of data across different groups or categories. * Identifying outliers: Box plots help identify outliers, which can be useful in detecting errors or unusual patterns in the data. * Analyzing skewness: Box plots can be used to analyze the skewness of a distribution, which can help identify if the data is symmetric or not. * Visualizing median and quartiles: Box plots provide a clear visualization of the median and quartiles, which can be useful in understanding the central tendency and variability of the data. * Detecting changes over time: Use box plots to detect changes in the distribution of data over time, which can be useful in identifying trends or patterns.
Example of Using Box Plot
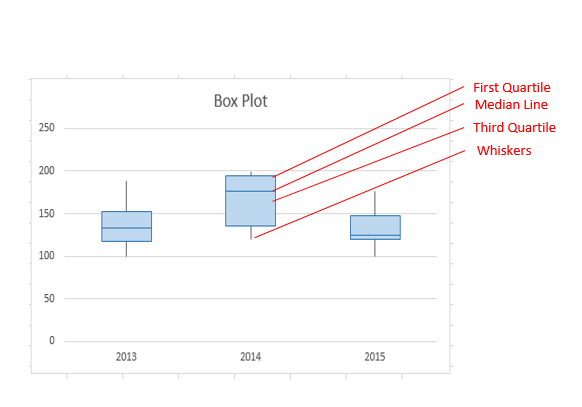
Suppose we have a dataset of exam scores for a class of students. We can use a box plot to visualize the distribution of scores and compare the performance of different groups of students.
| Group | Median | Q1 | Q3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 80 | 75 | 85 |
| B | 70 | 65 | 75 |
| C | 90 | 85 | 95 |
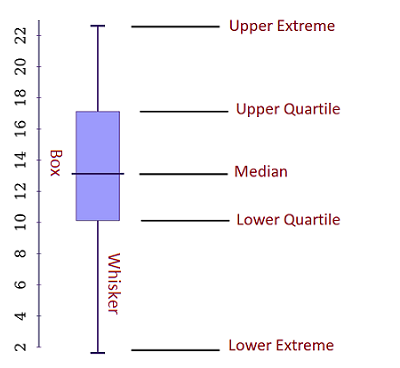
The box plot shows that Group C has the highest median score, while Group B has the lowest. The plot also shows that Group A has a wider range of scores than Group C.
Conclusion
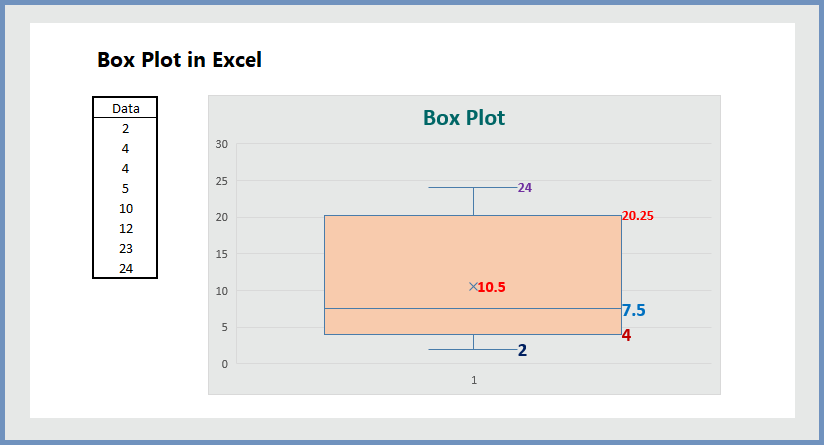
In summary, Excel box plots are a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data. By following the 5 ways to use Excel box plots outlined in this article, you can gain a deeper understanding of your data and make more informed decisions. Whether you are comparing distributions, identifying outliers, or detecting changes over time, box plots are an essential tool to have in your data analysis toolkit.
What is the purpose of a box plot?
+
The purpose of a box plot is to visualize the distribution of data and display the median, quartiles, and outliers in a dataset.
How do I create a box plot in Excel?
+
To create a box plot in Excel, select the data range, go to the “Insert” tab, click on “Insert Statistic Chart”, and select “Box and Whisker” chart.
What are the five key values displayed in a box plot?
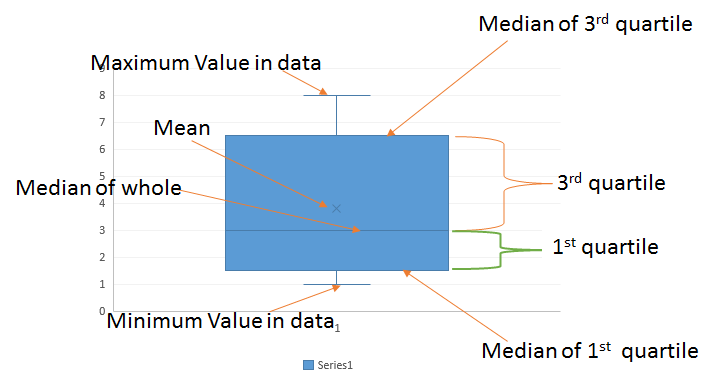
+
The five key values displayed in a box plot are the minimum, first quartile (Q1), median (Q2), third quartile (Q3), and maximum.