5 Ways To Graph
Introduction to Graphing

Graphing is a fundamental concept in mathematics and data analysis, used to visualize and understand the relationships between different variables. There are various ways to graph data, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we will explore five common methods of graphing, including their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
1. Line Graphs
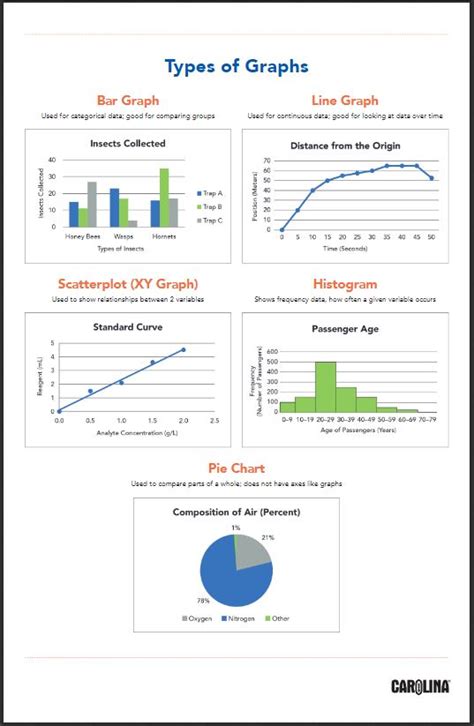
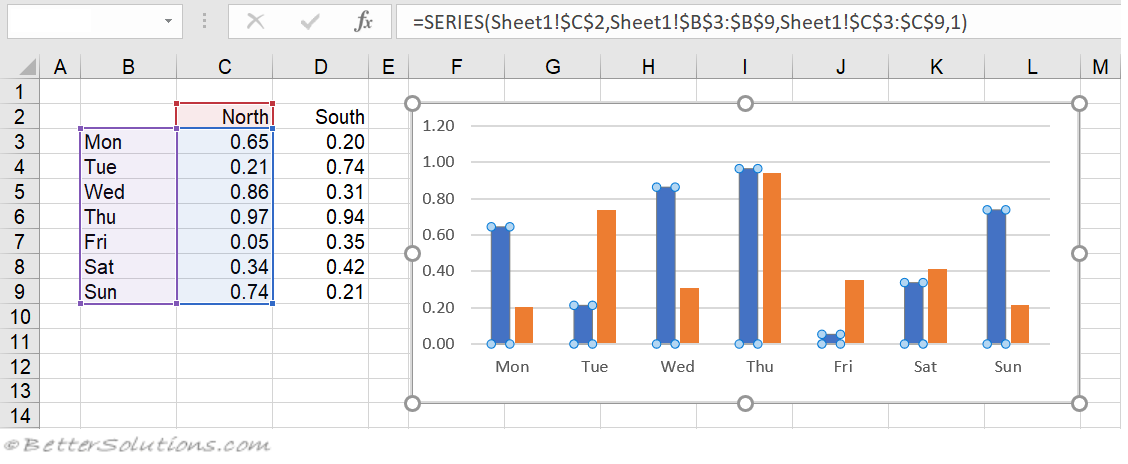
Line graphs are one of the most commonly used types of graphs, particularly for displaying trends over time. They consist of a series of points connected by lines, with each point representing a data point. Line graphs are useful for showing patterns, such as increases or decreases in data, and can be used to compare multiple datasets. The key elements of a line graph include: * X-axis: represents the independent variable * Y-axis: represents the dependent variable * Data points: represent the individual data values * Lines: connect the data points to show trends
2. Bar Graphs
Bar graphs are used to compare categorical data across different groups. They consist of rectangular bars of varying lengths, with each bar representing a category. Bar graphs are useful for displaying nominal or ordinal data and can be used to show differences between groups. The key elements of a bar graph include: * X-axis: represents the categories * Y-axis: represents the frequency or magnitude * Bars: represent the individual categories * Labels: provide additional information about each category
3. Pie Charts
Pie charts are circular graphs that show how different categories contribute to a whole. They consist of slices of varying sizes, with each slice representing a category. Pie charts are useful for displaying proportional data and can be used to show how different components make up a larger system. The key elements of a pie chart include: * Circle: represents the whole * Slices: represent the individual categories * Labels: provide additional information about each category * Legend: explains the colors or patterns used in the chart
4. Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to display the relationship between two continuous variables. They consist of a series of points, with each point representing a data point. Scatter plots are useful for showing correlations, such as positive or negative relationships, between variables. The key elements of a scatter plot include: * X-axis: represents one variable * Y-axis: represents the other variable * Points: represent the individual data values * Trend line: shows the overall pattern or relationship
5. Histograms
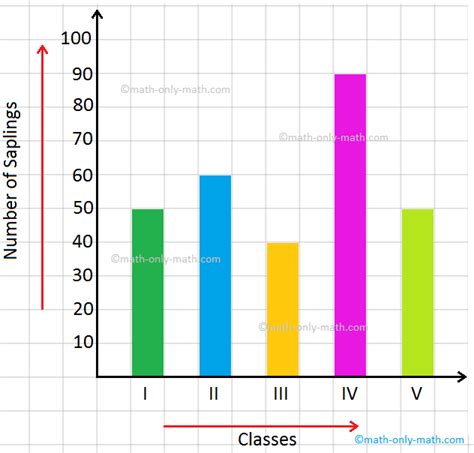
Histograms are used to display the distribution of a single continuous variable. They consist of rectangular bars of varying lengths, with each bar representing a range of values. Histograms are useful for showing the shape of a distribution, such as skewness or outliers, and can be used to understand the underlying patterns in data. The key elements of a histogram include: * X-axis: represents the variable * Y-axis: represents the frequency * Bars: represent the individual ranges * Labels: provide additional information about each range
📊 Note: When choosing a graph type, consider the nature of the data, the research question, and the audience. Different graphs are suited for different purposes, and selecting the right graph can help to effectively communicate the results.
To further illustrate the concepts, consider the following table:
| Graph Type | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Line Graph | Shows trends over time | Stock prices over a year |
| Bar Graph | Compares categorical data | Favorite colors among students |
| Pie Chart | Displays proportional data | Market share of different companies |
| Scatter Plot | Shows relationships between variables | Correlation between height and weight |
| Histogram | Displays distribution of a variable | Exam scores of a class |
In summary, graphing is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding data. By choosing the right graph type and considering the key elements, researchers and analysts can effectively communicate their results and insights. Whether using line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, or histograms, graphing provides a versatile and essential method for exploring and presenting data.
What is the purpose of graphing in data analysis?
+
The purpose of graphing in data analysis is to visualize and understand the relationships between different variables, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
How do I choose the right graph type for my data?

+
Consider the nature of the data, the research question, and the audience. Different graphs are suited for different purposes, such as showing trends, comparing categories, or displaying relationships.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when graphing data?
+
Common mistakes to avoid when graphing data include using the wrong graph type, mislabeling axes, and failing to consider the audience and purpose of the graph.